Generate images with AI
In this exercise, you use the the OpenAI DALL-E generative AI model to generate images. You’ll develop your app by using Azure AI Foundry and the Azure OpenAI service.
This exercise takes approximately 30 minutes.
Create an Azure AI Foundry project
Let’s start by creating an Azure AI Foundry project.
-
In a web browser, open the Azure AI Foundry portal at
https://ai.azure.comand sign in using your Azure credentials. Close any tips or quick start panes that are opened the first time you sign in, and if necessary use the Azure AI Foundry logo at the top left to navigate to the home page, which looks similar to the following image:
- In the home page, select + Create project.
- In the Create a project wizard, enter a valid name for your project and if an existing hub is suggested, choose the option to create a new one. Then review the Azure resources that will be automatically created to support your hub and project.
- Select Customize and specify the following settings for your hub:
- Hub name: A valid name for your hub
- Subscription: Your Azure subscription
- Resource group: Create or select a resource group
- Location: Select Help me choose and then select dalle in the Location helper window and use the recommended region*
- Connect Azure AI Services or Azure OpenAI: Create a new AI Services resource
- Connect Azure AI Search: Skip connecting
* Azure OpenAI resources are constrained by regional quotas. In the event of a quota limit being reached later in the exercise, there’s a possibility you may need to create another resource in a different region.
- Select Next and review your configuration. Then select Create and wait for the process to complete.
-
When your project is created, close any tips that are displayed and review the project page in Azure AI Foundry portal, which should look similar to the following image:
Deploy a DALL-E model
Now you’re ready to deploy a DALL-E model to support image-generation.
- In the toolbar at the top right of your Azure AI Foundry project page, use the Preview features icon to enable the Deploy models to Azure AI model inference service feature. This feature ensures your model deployment is available to the Azure AI Inference service, which you’ll use in your application code.
- In the pane on the left for your project, in the My assets section, select the Models + endpoints page.
- In the Models + endpoints page, in the Model deployments tab, in the + Deploy model menu, select Deploy base model.
- Search for the dall-e-3 model in the list, and then select and confirm it.
- Agree to the license agreement if prompted, and then deploy the model with the following settings by selecting Customize in the deployment details:
- Deployment name: A valid name for your model deployment
- Deployment type: Standard
- Deployment details: Use the default settings
- Wait for the deployment provisioning state to be Completed.
Test the model in the playground
Before creating a client application, let’s test the DALL-E model in the playground.
- In the page for the DALL-E model you deployed, select Open in playground (or in the Playgrounds page, open the Images playground).
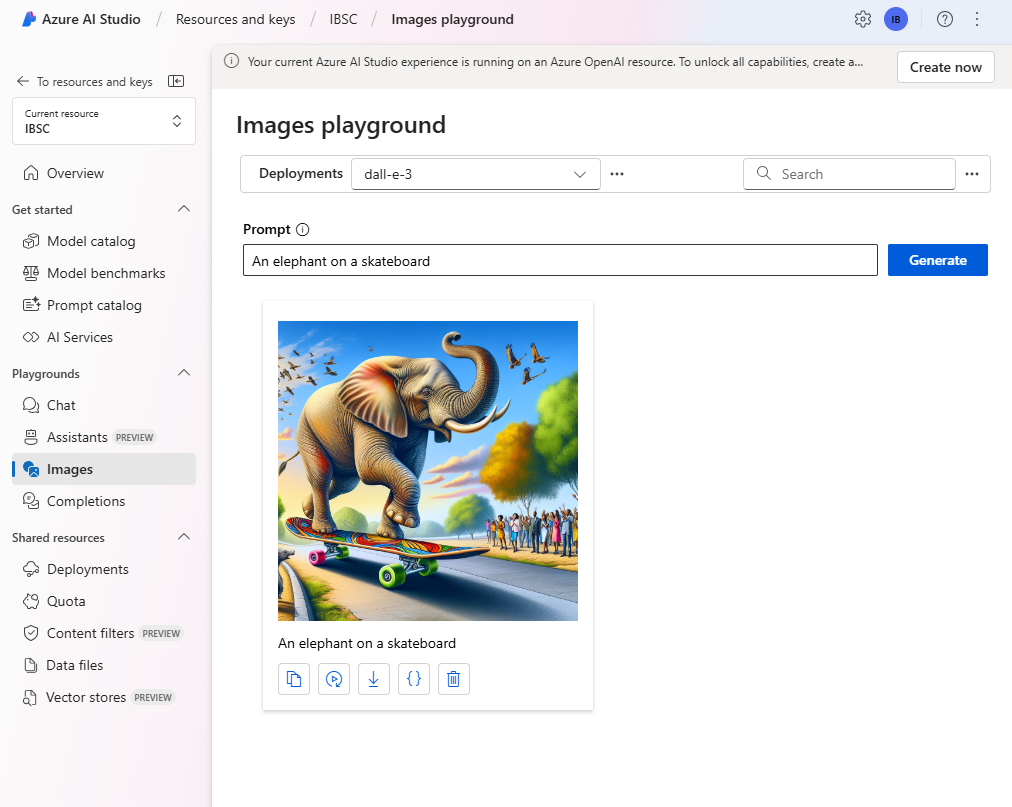
- Ensure your DALL-E model deployment is selected. Then, in the Prompt box, enter a prompt such as
Create an image of an robot eating spaghetti. -
Review the resulting image in the playground:
- Enter a follow-up prompt, such as
Show the robot in a restaurantand review the resulting image. - Continue testing with new prompts to refine the image until you are happy with it.
Create a client application
The model seems to work in the playground. Now you can use the Azure OpenAI SDK to use it in a client application.
Tip: You can choose to develop your solution using Python or Microsoft C#. Follow the instructions in the appropriate section for your chosen language.
Prepare the application configuration
- In the Azure AI Foundry portal, view the Overview page for your project.
- In the Project details area, note the Project connection string. You’ll use this connection string to connect to your project in a client application.
- Open a new browser tab (keeping the Azure AI Foundry portal open in the existing tab). Then in the new tab, browse to the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.com; signing in with your Azure credentials if prompted. -
Use the [>_] button to the right of the search bar at the top of the page to create a new Cloud Shell in the Azure portal, selecting a PowerShell environment. The cloud shell provides a command line interface in a pane at the bottom of the Azure portal.
Note: If you have previously created a cloud shell that uses a Bash environment, switch it to PowerShell.
-
In the cloud shell toolbar, in the Settings menu, select Go to Classic version (this is required to use the code editor).
Ensure you've switched to the classic version of the cloud shell before continuing.
-
In the cloud shell pane, enter the following commands to clone the GitHub repo containing the code files for this exercise (type the command, or copy it to the clipboard and then right-click in the command line and paste as plain text):
rm -r mslearn-openai -f git clone https://github.com/microsoftlearning/mslearn-openai mslearn-openaiTip: As you paste commands into the cloudshell, the ouput may take up a large amount of the screen buffer. You can clear the screen by entering the
clscommand to make it easier to focus on each task. -
After the repo has been cloned, navigate to the language-specific folder containing the application code files, based on the programming language of your choice (Python or C#):
Python
cd mslearn-openai/Labfiles/03-image-generation/PythonC#
cd mslearn-openai/Labfiles/03-image-generation/CSharp -
In the cloud shell command line pane, enter the following command to install the libraries you’ll use:
Python
python -m venv labenv ./labenv/bin/Activate.ps1 pip install python-dotenv azure-identity azure-ai-projects openai requestsC#
dotnet add package Azure.Identity dotnet add package Azure.AI.Projects --prerelease dotnet add package Azure.AI.OpenAI -
Enter the following command to edit the configuration file that has been provided:
Python
code .envC#
code appsettings.jsonThe file is opened in a code editor.
- In the code file, replace the your_project_endpoint placeholder with the connection string for your project (copied from the project Overview page in the Azure AI Foundry portal), and the your_model_deployment placeholder with the name you assigned to your dall-e-3 model deployment.
- After you’ve replaced the placeholders, use the CTRL+S command to save your changes and then use the CTRL+Q command to close the code editor while keeping the cloud shell command line open.
Write code to connect to your project and chat with your model
Tip: As you add code, be sure to maintain the correct indentation.
-
Enter the following command to edit the code file that has been provided:
Python
code dalle-client.pyC#
code Program.cs -
In the code file, note the existing statements that have been added at the top of the file to import the necessary SDK namespaces. Then, under the comment Add references, add the following code to reference the namespaces in the libraries you installed previously:
Python
# Add references from dotenv import load_dotenv from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential from azure.ai.projects import AIProjectClient from openai import AzureOpenAI import requestsC#
// Add references using Azure.Identity; using Azure.AI.Projects; using Azure.AI.OpenAI; using OpenAI.Images; - In the main function, under the comment Get configuration settings, note that the code loads the project connection string and model deployment name values you defined in the configuration file.
-
Under the comment Initialize the project client, add the following code to connect to your Azure AI Foundry project using the Azure credentials you are currently signed in with:
Python
# Initialize the project client project_client = AIProjectClient.from_connection_string( conn_str=project_connection, credential=DefaultAzureCredential())C#
// Initialize the project client var projectClient = new AIProjectClient(project_connection, new DefaultAzureCredential()); -
Under the comment Get an OpenAI client, add the following code to create a client object for chatting with a model:
Python
# Get an OpenAI client openai_client = project_client.inference.get_azure_openai_client(api_version="2024-06-01")C#
// Get an OpenAI client ConnectionResponse connection = projectClient.GetConnectionsClient().GetDefaultConnection(ConnectionType.AzureOpenAI, withCredential: true); var connectionProperties = connection.Properties as ConnectionPropertiesApiKeyAuth; AzureOpenAIClient openAIClient = new( new Uri(connectionProperties.Target), new AzureKeyCredential(connectionProperties.Credentials.Key)); ImageClient openAIimageClient = openAIClient.GetImageClient(model_deployment); -
Note that the code includes a loop to allow a user to input a prompt until they enter “quit”. Then in the loop section, under the comment Generate an image, add the following code to submit the prompt and retrieve the URL for the generated image from your model:
Python
# Generate an image result = openai_client.images.generate( model=model_deployment, prompt=input_text, n=1 ) json_response = json.loads(result.model_dump_json()) image_url = json_response["data"][0]["url"]C#
// Generate an image var imageGeneration = await openAIimageClient.GenerateImageAsync( input_text, new ImageGenerationOptions() { Size = GeneratedImageSize.W1024xH1024 } ); imageUrl= imageGeneration.Value.ImageUri; -
Note that the code in the remainder of the main function passes the image URL and a filename to a provided function, which downloads the generated image and saves it as a .png file.
- Use the CTRL+S command to save your changes to the code file and then use the CTRL+Q command to close the code editor while keeping the cloud shell command line open.
Run the client application
-
In the cloud shell command line pane, enter the following command to run the app:
Python
python dalle-client.pyC#
dotnet run - When prompted, enter a request for an image, such as
Create an image of a robot eating pizza. After a moment or two, the app should confirm that the image has been saved. -
Try a few more prompts. When you’re finished, enter
quitto exit the program.Note: In this simple app, we haven’t implemented logic to retain conversation history; so the model will treat each prompt as a new request with no context of the previous prompt.
-
To download and view the images that were generated by your app, use the cloud shell download command - specifying the .png file that was generated:
download ./images/image_1.pngThe download command creates a popup link at the bottom right of your browser, which you can select to download and open the file.
Summary
In this exercise, you used Azure AI Foundry and the Azure OpenAI SDK to create a client application uses a DALL-E model to generate images.
Clean up
If you’ve finished exploring DALL-E, you should delete the resources you have created in this exercise to avoid incurring unnecessary Azure costs.
- Return to the browser tab containing the Azure portal (or re-open the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.comin a new browser tab) and view the contents of the resource group where you deployed the resources used in this exercise. - On the toolbar, select Delete resource group.
- Enter the resource group name and confirm that you want to delete it.