Implement interactive authentication with MSAL.NET
In this exercise, you register an application in Microsoft Entra ID, then create a .NET console application that uses MSAL.NET to perform interactive authentication and acquire an access token for Microsoft Graph. You learn how to configure authentication scopes, handle user consent, and see how tokens are cached for subsequent runs.
Tasks performed in this exercise:
- Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform
- Create a .NET console app that implements the PublicClientApplicationBuilder class to configure authentication.
- Acquire a token interactively using the user.read Microsoft Graph permission.
This exercise takes approximately 15 minutes to complete.
Before you start
To complete the exercise, you need:
-
An Azure subscription. If you don't already have one, you can sign up for one.
-
Visual Studio Code on one of the supported platforms.
-
.NET 8 or greater.
-
C# Dev Kit for Visual Studio Code.
Register a new application
-
In your browser navigate to the Azure portal https://portal.azure.com; signing in with your Azure credentials if prompted.
-
In the portal, search for and select App registrations.
-
Select + New registration, and when the Register an application page appears, enter your application's registration information:
Field Value Name Enter myMsalApplicationSupported account types Select Accounts in this organizational directory only Redirect URI (optional) Select Public client/native (mobile & desktop) and enter http://localhostin the box to the right. -
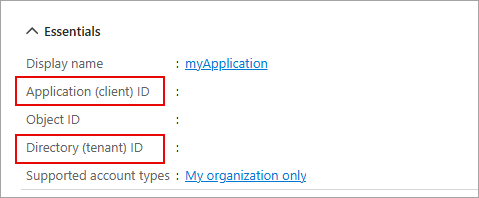
Select Register. Microsoft Entra ID assigns a unique application (client) ID to your app, and you're taken to your application's Overview page.
-
In the Essentials section of the Overview page record the Application (client) ID and the Directory (tenant) ID. The information is needed for the application.
Create a .NET console app to acquire a token
Now that the needed resources are deployed to Azure the next step is to set up the console application. The following steps are performed in your local environment.
-
Create a folder named authapp, or a name of your choosing, for the project.
-
Launch Visual Studio Code and select File > Open folder... and select the project folder.
-
Select View > Terminal to open a terminal.
-
Run the following command in the VS Code terminal to create the .NET console application.
dotnet new console -
Run the following commands to add the Microsoft.Identity.Client and dotenv.net packages to the project.
dotnet add package Microsoft.Identity.Client dotnet add package dotenv.net
Configure the console application
In this section you create, and edit, a .env file to hold the secrets you recorded earlier.
-
Select File > New file... and create a file named .env in the project folder.
-
Open the .env file and add the following code. Replace YOUR_CLIENT_ID, and YOUR_TENANT_ID with the values you recorded earlier.
CLIENT_ID="YOUR_CLIENT_ID" TENANT_ID="YOUR_TENANT_ID" -
Press ctrl+s to save your changes.
Add the starter code for the project
-
Open the Program.cs file and replace any existing contents with the following code. Be sure to review the comments in the code.
using Microsoft.Identity.Client; using dotenv.net; // Load environment variables from .env file DotEnv.Load(); var envVars = DotEnv.Read(); // Retrieve Azure AD Application ID and tenant ID from environment variables string _clientId = envVars["CLIENT_ID"]; string _tenantId = envVars["TENANT_ID"]; // ADD CODE TO DEFINE SCOPES AND CREATE CLIENT // ADD CODE TO ACQUIRE AN ACCESS TOKEN -
Press ctrl+s to save your changes.
Add code to complete the application
-
Locate the // ADD CODE TO DEFINE SCOPES AND CREATE CLIENT comment and add the following code directly after the comment. Be sure to review the comments in the code.
// Define the scopes required for authentication string[] _scopes = { "User.Read" }; // Build the MSAL public client application with authority and redirect URI var app = PublicClientApplicationBuilder.Create(_clientId) .WithAuthority(AzureCloudInstance.AzurePublic, _tenantId) .WithDefaultRedirectUri() .Build(); -
Locate the // ADD CODE TO ACQUIRE AN ACCESS TOKEN comment and add the following code directly after the comment. Be sure to review the comments in the code.
// Attempt to acquire an access token silently or interactively AuthenticationResult result; try { // Try to acquire token silently from cache for the first available account var accounts = await app.GetAccountsAsync(); result = await app.AcquireTokenSilent(_scopes, accounts.FirstOrDefault()) .ExecuteAsync(); } catch (MsalUiRequiredException) { // If silent token acquisition fails, prompt the user interactively result = await app.AcquireTokenInteractive(_scopes) .ExecuteAsync(); } // Output the acquired access token to the console Console.WriteLine($"Access Token:\n{result.AccessToken}"); -
Press ctrl+s to save the file, then ctrl+q to exit the editor.
Run the application
Now that the app is complete it's time to run it.
-
Start the application by running the following command:
dotnet run -
The app opens the default browser prompting you to select the account you want to authenticate with. If there are multiple accounts listed select the one associated with the tenant used in the app.
-
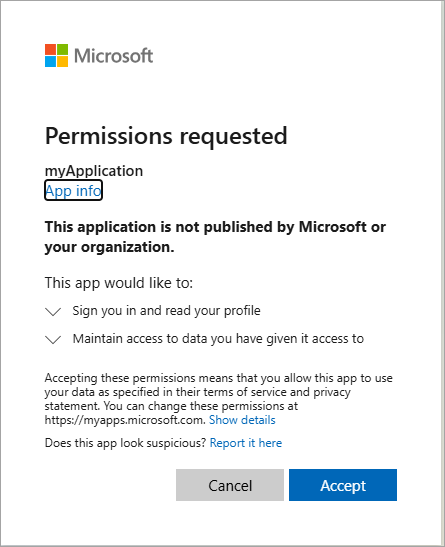
If this is the first time you've authenticated to the registered app you receive a Permissions requested notification asking you to approve the app to sign you in and read your profile, and maintain access to data you have given it access to. Select Accept.
-
You should see the results similar to the example below in the console.
Access Token: eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJub25jZSI6IlZF......... -
Start the application a second time and notice you no longer receive the Permissions requested notification. The permission you granted earlier was cached. Note: If you have mutliple accounts, and With some account configurations, you might see the notification again.
Clean up resources
Now that you finished the exercise, you should delete the cloud resources you created to avoid unnecessary resource usage.
- In your browser navigate to the Azure portal https://portal.azure.com; signing in with your Azure credentials if prompted.
- Navigate to the resource group you created and view the contents of the resources used in this exercise.
- On the toolbar, select Delete resource group.
- Enter the resource group name and confirm that you want to delete it.
CAUTION: Deleting a resource group deletes all resources contained within it. If you chose an existing resource group for this exercise, any existing resources outside the scope of this exercise will also be deleted.