Develop a multi-agent solution (deprecated)
In this exercise, you’ll create a project that orchestrates multiple AI agents using Microsoft Foundry Agent Service. You’ll design an AI solution that assists with ticket triage. The connected agents will assess the ticket’s priority, suggest a team assignment, and determine the level of effort required to complete the ticket. Let’s get started!
Tip: The code used in this exercise is based on the for Foundry SDK for Python. You can develop similar solutions using the SDKs for Microsoft .NET, JavaScript, and Java. Refer to Foundry SDK client libraries for details.
This exercise should take approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Note: Some of the technologies used in this exercise are in preview or in active development. You may experience some unexpected behavior, warnings, or errors.
Create a Foundry project
Let’s start by creating a Foundry project.
-
In a web browser, open the Foundry portal at
https://ai.azure.comand sign in using your Azure credentials. Close any tips or quick start panes that are opened the first time you sign in, and if necessary use the Foundry logo at the top left to navigate to the home page, which looks similar to the following image (close the Help pane if it’s open):
Important: Make sure the New Foundry toggle is Off for this lab.
- In the home page, select Create an agent.
- When prompted to create a project, enter a valid name for your project and expand Advanced options.
- Confirm the following settings for your project:
- Foundry resource: A valid name for your Foundry resource
- Subscription: Your Azure subscription
- Resource group: Create or select a resource group
- Region: Select any AI Foundry recommended*
* Some Azure AI resources are constrained by regional model quotas. In the event of a quota limit being exceeded later in the exercise, there’s a possibility you may need to create another resource in a different region.
- Select Create and wait for your project to be created.
-
If prompted, deploy a gpt-4o model using either the Global Standard or Standard deployment option (depending on your quota availability).
Note: If quota is available, a GPT-4o base model may be deployed automatically when creating your Agent and project.
-
When your project is created, the Agents playground will be opened.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, select Overview to see the main page for your project; which looks like this:
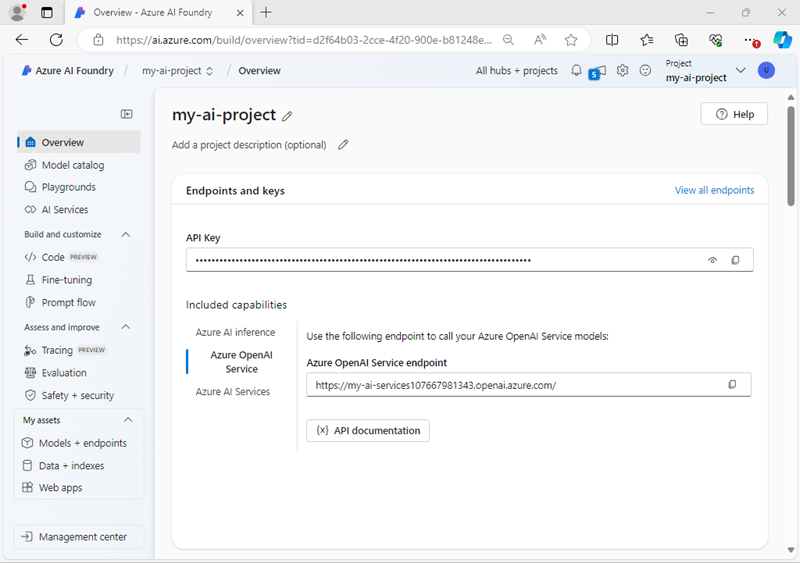
- Copy the Foundry project endpoint values to a notepad, as you’ll use them to connect to your project in a client application.
Create an AI Agent client app
Now you’re ready to create a client app that defines the agents and instructions. Some code is provided for you in a GitHub repository.
Prepare the environment
-
Open a new browser tab (keeping the Foundry portal open in the existing tab). Then in the new tab, browse to the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.com; signing in with your Azure credentials if prompted.Close any welcome notifications to see the Azure portal home page.
-
Use the [>_] button to the right of the search bar at the top of the page to create a new Cloud Shell in the Azure portal, selecting a PowerShell environment with no storage in your subscription.
The cloud shell provides a command-line interface in a pane at the bottom of the Azure portal. You can resize or maximize this pane to make it easier to work in.
Note: If you have previously created a cloud shell that uses a Bash environment, switch it to PowerShell.
-
In the cloud shell toolbar, in the Settings menu, select Go to Classic version (this is required to use the code editor).
Ensure you've switched to the classic version of the cloud shell before continuing.
-
In the cloud shell pane, enter the following commands to clone the GitHub repo containing the code files for this exercise (type the command, or copy it to the clipboard and then right-click in the command line and paste as plain text):
rm -r ai-agents -f git clone https://github.com/MicrosoftLearning/mslearn-ai-agents ai-agentsTip: As you enter commands into the cloud shell, the output may take up a large amount of the screen buffer and the cursor on the current line may be obscured. You can clear the screen by entering the
clscommand to make it easier to focus on each task. -
When the repo has been cloned, enter the following command to change the working directory to the folder containing the code files and list them all.
cd ai-agents/Labfiles/03b-build-multi-agent-solution/Python ls -a -lThe provided files include application code and a file for configuration settings.
Configure the application settings
-
In the cloud shell command-line pane, enter the following command to install the libraries you’ll use:
python -m venv labenv ./labenv/bin/Activate.ps1 pip install -r requirements.txt azure-ai-projects azure-ai-agents -
Enter the following command to edit the configuration file that is provided:
code .envThe file is opened in a code editor.
-
In the code file, replace the your_project_endpoint placeholder with the endpoint for your project (copied from the project Overview page in the Foundry portal), and the your_model_deployment placeholder with the name you assigned to your gpt-4o model deployment (which by default is
gpt-4o). -
After you’ve replaced the placeholders, use the CTRL+S command to save your changes and then use the CTRL+Q command to close the code editor while keeping the cloud shell command line open.
Create AI agents
Now you’re ready to create the agents for your multi-agent solution! Let’s get started!
-
Enter the following command to edit the agent_triage.py file:
code agent_triage.py -
Review the code in the file, noting that it contains strings for each agent name and instructions.
-
Find the comment Add references and add the following code to import the classes you’ll need:
# Add references from azure.ai.agents import AgentsClient from azure.ai.agents.models import ConnectedAgentTool, MessageRole, ListSortOrder, ToolSet, FunctionTool from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential -
Note that code to load the project endpoint and model name from your environment variables has been provided.
-
Find the comment Connect to the agents client, and add the following code to create an AgentsClient connected to your project:
# Connect to the agents client agents_client = AgentsClient( endpoint=project_endpoint, credential=DefaultAzureCredential( exclude_environment_credential=True, exclude_managed_identity_credential=True ), )Now you’ll add code that uses the AgentsClient to create multiple agents, each with a specific role to play in processing a support ticket.
Tip: When adding subsequent code, be sure to maintain the right level of indentation under the
using agents_client:statement. -
Find the comment Create an agent to prioritize support tickets, and enter the following code (being careful to retain the right level of indentation):
# Create an agent to prioritize support tickets priority_agent_name = "priority_agent" priority_agent_instructions = """ Assess how urgent a ticket is based on its description. Respond with one of the following levels: - High: User-facing or blocking issues - Medium: Time-sensitive but not breaking anything - Low: Cosmetic or non-urgent tasks Only output the urgency level and a very brief explanation. """ priority_agent = agents_client.create_agent( model=model_deployment, name=priority_agent_name, instructions=priority_agent_instructions ) -
Find the comment Create an agent to assign tickets to the appropriate team, and enter the following code:
# Create an agent to assign tickets to the appropriate team team_agent_name = "team_agent" team_agent_instructions = """ Decide which team should own each ticket. Choose from the following teams: - Frontend - Backend - Infrastructure - Marketing Base your answer on the content of the ticket. Respond with the team name and a very brief explanation. """ team_agent = agents_client.create_agent( model=model_deployment, name=team_agent_name, instructions=team_agent_instructions ) -
Find the comment Create an agent to estimate effort for a support ticket, and enter the following code:
# Create an agent to estimate effort for a support ticket effort_agent_name = "effort_agent" effort_agent_instructions = """ Estimate how much work each ticket will require. Use the following scale: - Small: Can be completed in a day - Medium: 2-3 days of work - Large: Multi-day or cross-team effort Base your estimate on the complexity implied by the ticket. Respond with the effort level and a brief justification. """ effort_agent = agents_client.create_agent( model=model_deployment, name=effort_agent_name, instructions=effort_agent_instructions )So far, you’ve created three agents; each of which has a specific role in triaging a support ticket. Now let’s create ConnectedAgentTool objects for each of these agents so they can be used by other agents.
-
Find the comment Create connected agent tools for the support agents, and enter the following code:
# Create connected agent tools for the support agents priority_agent_tool = ConnectedAgentTool( id=priority_agent.id, name=priority_agent_name, description="Assess the priority of a ticket" ) team_agent_tool = ConnectedAgentTool( id=team_agent.id, name=team_agent_name, description="Determines which team should take the ticket" ) effort_agent_tool = ConnectedAgentTool( id=effort_agent.id, name=effort_agent_name, description="Determines the effort required to complete the ticket" )Now you’re ready to create a primary agent that will coordinate the ticket triage process, using the connected agents as required.
-
Find the comment Create an agent to triage support ticket processing by using connected agents, and enter the following code:
# Create an agent to triage support ticket processing by using connected agents triage_agent_name = "triage-agent" triage_agent_instructions = """ Triage the given ticket. Use the connected tools to determine the ticket's priority, which team it should be assigned to, and how much effort it may take. """ triage_agent = agents_client.create_agent( model=model_deployment, name=triage_agent_name, instructions=triage_agent_instructions, tools=[ priority_agent_tool.definitions[0], team_agent_tool.definitions[0], effort_agent_tool.definitions[0] ] )Now that you have defined a primary agent, you can submit a prompt to it and have it use the other agents to triage a support issue.
-
Find the comment Use the agents to triage a support issue, and enter the following code:
# Use the agents to triage a support issue print("Creating agent thread.") thread = agents_client.threads.create() # Create the ticket prompt prompt = input("\nWhat's the support problem you need to resolve?: ") # Send a prompt to the agent message = agents_client.messages.create( thread_id=thread.id, role=MessageRole.USER, content=prompt, ) # Run the thread usng the primary agent print("\nProcessing agent thread. Please wait.") run = agents_client.runs.create_and_process(thread_id=thread.id, agent_id=triage_agent.id) if run.status == "failed": print(f"Run failed: {run.last_error}") # Fetch and display messages messages = agents_client.messages.list(thread_id=thread.id, order=ListSortOrder.ASCENDING) for message in messages: if message.text_messages: last_msg = message.text_messages[-1] print(f"{message.role}:\n{last_msg.text.value}\n") -
Find the comment Clean up, and enter the following code to delete the agents when they are no longer required:
# Clean up print("Cleaning up agents:") agents_client.delete_agent(triage_agent.id) print("Deleted triage agent.") agents_client.delete_agent(priority_agent.id) print("Deleted priority agent.") agents_client.delete_agent(team_agent.id) print("Deleted team agent.") agents_client.delete_agent(effort_agent.id) print("Deleted effort agent.") -
Use the CTRL+S command to save your changes to the code file. You can keep it open (in case you need to edit the code to fix any errors) or use the CTRL+Q command to close the code editor while keeping the cloud shell command line open.
Sign into Azure and run the app
Now you’re ready to run your code and watch your AI agents collaborate.
-
In the cloud shell command-line pane, enter the following command to sign into Azure.
az loginYou must sign into Azure - even though the cloud shell session is already authenticated.
Note: In most scenarios, just using az login will be sufficient. However, if you have subscriptions in multiple tenants, you may need to specify the tenant by using the –tenant parameter. See Sign into Azure interactively using the Azure CLI for details.
-
When prompted, follow the instructions to open the sign-in page in a new tab and enter the authentication code provided and your Azure credentials. Then complete the sign in process in the command line, selecting the subscription containing your Foundry hub if prompted.
-
After you have signed in, enter the following command to run the application:
python agent_triage.py -
Enter a prompt, such as
Users can't reset their password from the mobile app.After the agents process the prompt, you should see some output similar to the following:
Creating agent thread. Processing agent thread. Please wait. MessageRole.USER: Users can't reset their password from the mobile app. MessageRole.AGENT: ### Ticket Assessment - **Priority:** High — This issue blocks users from resetting their passwords, limiting access to their accounts. - **Assigned Team:** Frontend Team — The problem lies in the mobile app's user interface or functionality. - **Effort Required:** Medium — Resolving this problem involves identifying the root cause, potentially updating the mobile app functionality, reviewing API/backend integration, and testing to ensure compatibility across Android/iOS platforms. Cleaning up agents: Deleted triage agent. Deleted priority agent. Deleted team agent. Deleted effort agent.You can try modifying the prompt using a different ticket scenario to see how the agents collaborate. For example, “Investigate occasional 502 errors from the search endpoint.”
Clean up
If you’ve finished exploring Azure AI Agent Service, you should delete the resources you have created in this exercise to avoid incurring unnecessary Azure costs.
-
Return to the browser tab containing the Azure portal (or re-open the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.comin a new browser tab) and view the contents of the resource group where you deployed the resources used in this exercise. -
On the toolbar, select Delete resource group.
-
Enter the resource group name and confirm that you want to delete it.