Transform data using Spark in Synapse Analytics
Data engineers often use Spark notebooks as one of their preferred tools to perform extract, transform, and load (ETL) or extract, load, and transform (ELT) activities that transform data from one format or structure to another.
In this exercise, you’ll use a Spark notebook in Azure Synapse Analytics to transform data in files.
This exercise should take approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Before you start
You’ll need an Azure subscription in which you have administrative-level access.
Provision an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace
You’ll need an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace with access to data lake storage and a Spark pool.
In this exercise, you’ll use a combination of a PowerShell script and an ARM template to provision an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace.
- Sign into the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.com. -
Use the [>_] button to the right of the search bar at the top of the page to create a new Cloud Shell in the Azure portal, selecting a PowerShell environment and creating storage if prompted. The cloud shell provides a command line interface in a pane at the bottom of the Azure portal, as shown here:
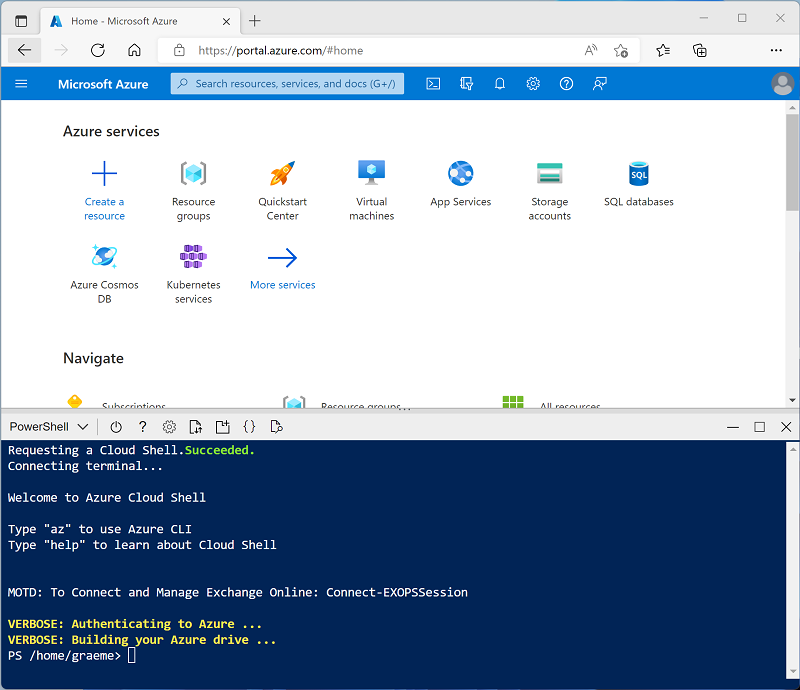
Note: If you have previously created a cloud shell that uses a Bash environment, use the the drop-down menu at the top left of the cloud shell pane to change it to PowerShell.
-
Note that you can resize the cloud shell by dragging the separator bar at the top of the pane, or by using the —, ◻, and X icons at the top right of the pane to minimize, maximize, and close the pane. For more information about using the Azure Cloud Shell, see the Azure Cloud Shell documentation.
-
In the PowerShell pane, enter the following commands to clone this repo:
rm -r dp-203 -f git clone https://github.com/MicrosoftLearning/dp-203-azure-data-engineer dp-203 -
After the repo has been cloned, enter the following commands to change to the folder for this exercise and run the setup.ps1 script it contains:
cd dp-203/Allfiles/labs/06 ./setup.ps1 - If prompted, choose which subscription you want to use (this will only happen if you have access to multiple Azure subscriptions).
-
When prompted, enter a suitable password to be set for the Azure Synapse SQL pool.
Note: Be sure to remember this password!
- Wait for the script to complete - this typically takes around 10 minutes, but in some cases may take longer. While you are waiting, review the Apache Spark in Azure Synapse Analytics Core Concepts article in the Azure Synapse Analytics documentation.
Use a Spark notebook to transform data
- After the deployment script has completed, in the Azure portal, go to the dp203-xxxxxxx resource group that it created, and notice that this resource group contains your Synapse workspace, a Storage account for your data lake, and an Apache Spark pool.
- Select your Synapse workspace, and in its Overview page, in the Open Synapse Studio card, select Open to open Synapse Studio in a new browser tab; signing in if prompted.
- On the left side of Synapse Studio, use the ›› icon to expand the menu - this reveals the different pages within Synapse Studio that you’ll use to manage resources and perform data analytics tasks.
- On the Manage page, select the Apache Spark pools tab and note that a Spark pool with a name similar to sparkxxxxxxx has been provisioned in the workspace.
- On the Data page, view the Linked tab and verify that your workspace includes a link to your Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 storage account, which should have a name similar to synapsexxxxxxx (Primary - datalakexxxxxxx).
- Expand your storage account and verify that it contains a file system container named files (Primary).
- Select the files container, and note that it contains folders named data and synapse. The synapse folder is used by Azure Synapse, and the data folder contains the data files you are going to query.
- Open the data folder and observe that it contains .csv files for three years of sales data.
- Right-click any of the files and select Preview to see the data it contains. Note that the files contain a header row, so you can select the option to display column headers.
-
Close the preview. Then download the Spark Transform.ipynb from from Allfiles/labs/06/notebooks
Note: It’s best to copy this text using the ctrl+a then ctrl+c and pasting into a tool using ctrl+v, such as, notepad and then using file, save as Spark Transform.ipynb with a filetype of all files. You can also download the file by clicking on it, then selecting the ellipsis (…) and then download, remembering where you saved it.
-
Then on Develop page, expand Notebooks click on the + Import options
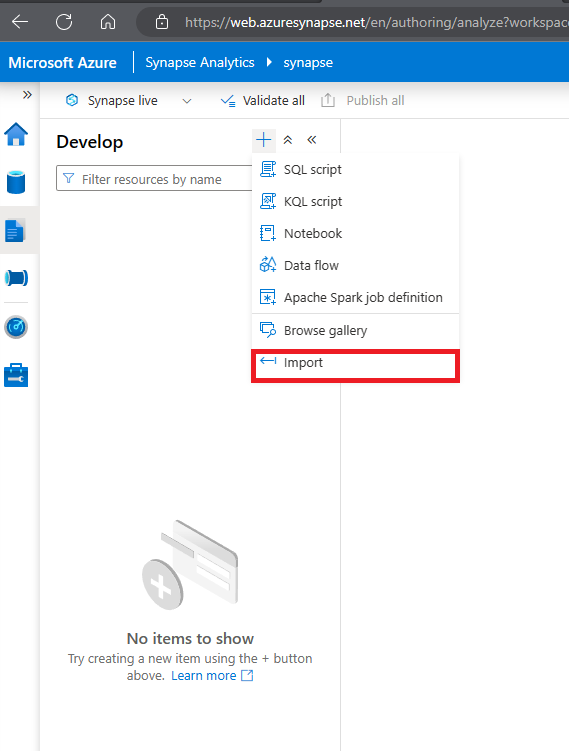
- Select the file you just downloaded and saved as Spark Transfrom.ipynb.
- Attach the notebook to your sparkxxxxxxx Spark pool.
-
Review the notes in the notebook and run the code cells.
Note: The first code cell will take a few minutes to run because the Spark pool must be started. Subsequent cells will run more quickly.
Delete Azure resources
If you’ve finished exploring Azure Synapse Analytics, you should delete the resources you’ve created to avoid unnecessary Azure costs.
- Close the Synapse Studio browser tab and return to the Azure portal.
- On the Azure portal, on the Home page, select Resource groups.
- Select the dp203-xxxxxxx resource group for your Synapse Analytics workspace (not the managed resource group), and verify that it contains the Synapse workspace, storage account, and Spark pool for your workspace.
- At the top of the Overview page for your resource group, select Delete resource group.
-
Enter the dp203-xxxxxxx resource group name to confirm you want to delete it, and select Delete.
After a few minutes, your Azure Synapse workspace resource group and the managed workspace resource group associated with it will be deleted.