Module 4 Lesson 1- Lab 2B: Configuring Omnichannel
Overview
As stated in the Lab 2A, Lamna Healthcare Company is seeking to streamline their patient engagement capabilities by implementing Azure Health Bot to help improve processes and services, such as entering medication requests. By allowing patients to interact with this service, Lamna Healthcare Company will move one step closer to their goal of improving patient outcomes while reducing overall costs.
In this lab, you’ll play the role of a Lamna Healthcare IT developer and use the Azure Health Bot you configured in Lab2A to integrate with Dynamics 365 Omnichannel. This will complete the work for a medication refill scenario.
Assign the Omnichannel agent security role
To assign the Omnichannel agent security role, follow these steps:
-
While in an InPrivate or Incognito browser, go to Microsoft Power Apps
-
Select your environment from the Environment dropdown menu in the upper right.
-
Select the gear icon in the upper-right corner and then select Advanced settings.
- A new window should open showing the Business Management section of Dynamics 365. If loading takes a while, reload the page.
- On the upper command bar next to Dynamics 365, select Settings to open the dropdown menu. Select Security in the third column under System.
- Under Security, select Users.
- Switch the grid view dropdown menu from Omnichannel Users to Enabled Users so that you can view the user in the list.
- In the Enabled Users list, scroll or use the search bar to find your user.
- Select your user for the training and then select Manage Roles on the upper command bar.
- Select the Omnichannel agent role to assign to your user and then select OK.
You’ve now assigned the correct Omnichannel agent role to the user, which will allow you to be a live agent in Omnichannel.
Task: Create a Health Bot user in Dynamics 365 Customer Service
You need to set up two users in Omnichannel for Customer Service:
-
Health Bot User - The Azure Health Bot user that you created in the previous exercise. This configuration will allow you to assign the bot as a user and take initial messages through live chat.
-
Omnichannel Agent User - The current user account that you’ve used to sign in to Dynamics 365. This configuration will allow you to be a live agent in Customer Service who receives messages from portal users through Azure bot escalations.
In this task, you’ll create a bot user, which will help you connect Azure Health Bot with Omnichannel live chat.
-
Open a new tab and go to Power Platform admin URL - Microsoft Power Platform admin center.
-
Select Environments from the left navigation pane. Search for and select your Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare environment from the list.
- On your Environments > Details page, select the Settings button on the upper command bar.
- Expand Users + permissions and then select Application users.
- Select the + New app user button to create a new application user.
- Select + Add an app on the Create a new app user page.
- Paste the Application ID (the Application (client) ID that you obtained in the Azure portal for the supplied MCH Application ID) into the search box and then select the app from the list. You can also search for mch. Select Add.
- Select a Business unit from the dropdown list (the options in the list will be unique for each Dynamics 365 environment). Select Create in the lower right of the page.
-
Return to the Dynamics 365 User page that you previously accessed through Advanced settings. Switch the view to Enabled Users if you’re not already on it. Clear the search terms, if any.
-
While in the Enabled Users list, search for MCH Application ID or scroll to find the bot app user. Double-click the user or select the row and then select Edit.
- Above the username, change the form type from User to Application User.
A new form will appear, and the User type should show as Application user.
- In the User Information section, change the User type from Application user to Bot application user. A new field called Bot application ID will display.
- Add your details to the Bot application ID. This ID is the Azure Health Bot ID that you previously noted when you enabled the Teams and Omnichannel channels. This field displays after Bot application user has been selected as the User type.
- Select Manage Roles on the command bar.
- Assign the Omnichannel agent role to the bot user as you did for your own user in the previous task. This action will allow the bot to act as an omnichannel agent like your user.
- Select OmniChannel Administrator role for your user ID and MCH Application Id users.
You’ve successfully created a bot user and have assigned the Omnichannel agent role to it.
Task: Create and set up human agent queues
You can use queues to collect and distribute workload among agents. As a result, agents will be added as members to the queues and the workload will be distributed among the agents based on assignment methods. For more information, see Manage queues for unified routing.
In this task, you’ll create the omnichannel queue that’s necessary for communicating with a human agent.
- Switch back to the tab with Power Apps select Apps in the left navigation pane and open the Customer Service admin center app
- You should be on the Home page. Select Guided channel setup on the left navigation pane and select Start new.
- On the Name your setup page, in the Setup name field, enter the name as Healthcare Training. Select Next.
- Select Chat as the channel type. Select Next.
- Select Continue setup on the Summary page.
- Select Next on the following two screens, which discuss creating user accounts and assigning security roles.
-
In the Define a queue page, create a queue called Escalate to Human, which will manage and redirect the incoming messages from a user to a Customer Service (human) agent when the bot sends the user through to a live agent. Create the new queue with the following details:
o Name - Escalate to Human
o Type - It will default to Messaging
-
Select Next.
- Select your user to add to the queue. Select Next.
You’ve now created the necessary queue to escalate to a human agent and have added your user to the messaging queue. Now, you can create the workstream to initially route to a virtual bot, along with routing rules to direct the user to the Escalate to Human queue in the proper conditions.
Task: Update the live workstream with context variables and routing rules
A workstream is a container to enrich, route, and assign work items, and it’s associated with a channel, such as live chat, voice, or case. After a bot has been added to a workstream, the incoming work item will be routed to the selected bot at runtime based on classification rules. For more information, see Create workstreams for unified routing.
In this task, you’ll set up basic chat routing with a new workstream. This setup will allow users to chat with a bot user initially and then route to a live human agent in the proper situation.
You’ll complete the following tasks:
-
Create a new channel and workstream.
-
Turn on proactive chat for the channel.
-
Add a bot for initial routing: Initial customer conversation is directed to the Azure Health Bot.
-
Create a context variable and routing rule to escalate to a human agent. When context variable EscalateToAgent is present and set to 1, you’ll route to the Escalate to Human queue that you previously set up with your user so that an agent can continue the conversation.
-
While continuing the guided setup from the previous task, enter a Chat name and Chat language for your channel and a workstream Name. Keep the Work distribution mode as Push and then select Next.
o Chat name - Chat Widget
o Workstream Name - Chat Workstream
- Define a ruleset that will allow work from this channel to be routed to the Escalate to Human queue. Name the Routing rules as Human Agent and the Rule item as Human Agent Rule. Select Next.
Note – On Define a Chatbot page select Skip for now and select Next.
- It will take a moment for the system to create the chat channel and workstream. When the process is complete, make sure that you Copy the chat widget snippet code and store it for later. Select Go to home.
- You still need to set up a few components for the routing to happen correctly:
o Add the bot user in the default messaging queue so that conversations initially route to the bot.
o Add the default messaging queue as the fallback queue for the new workstream.
o Define the routing rule in the workstream for escalating to a human agent.
- Go to Overview on the left navigation. Select Chat in the Channels section to view all chat channels.
- Select the newly created chat channel, Chat Widget, and then select Edit on the command bar.
- In the Chat channel settings form, select the Chat widget tab and then turn on Proactive chat. This setting will allow the bot to prompt the user on the website where it’s embedded. Select Copy to copy the chat widget code and store it for later use, if you haven’t done so already. Select Save and close.
- Return to Overview on the left navigation pane. Scroll down to Workstreams and then select Chat.
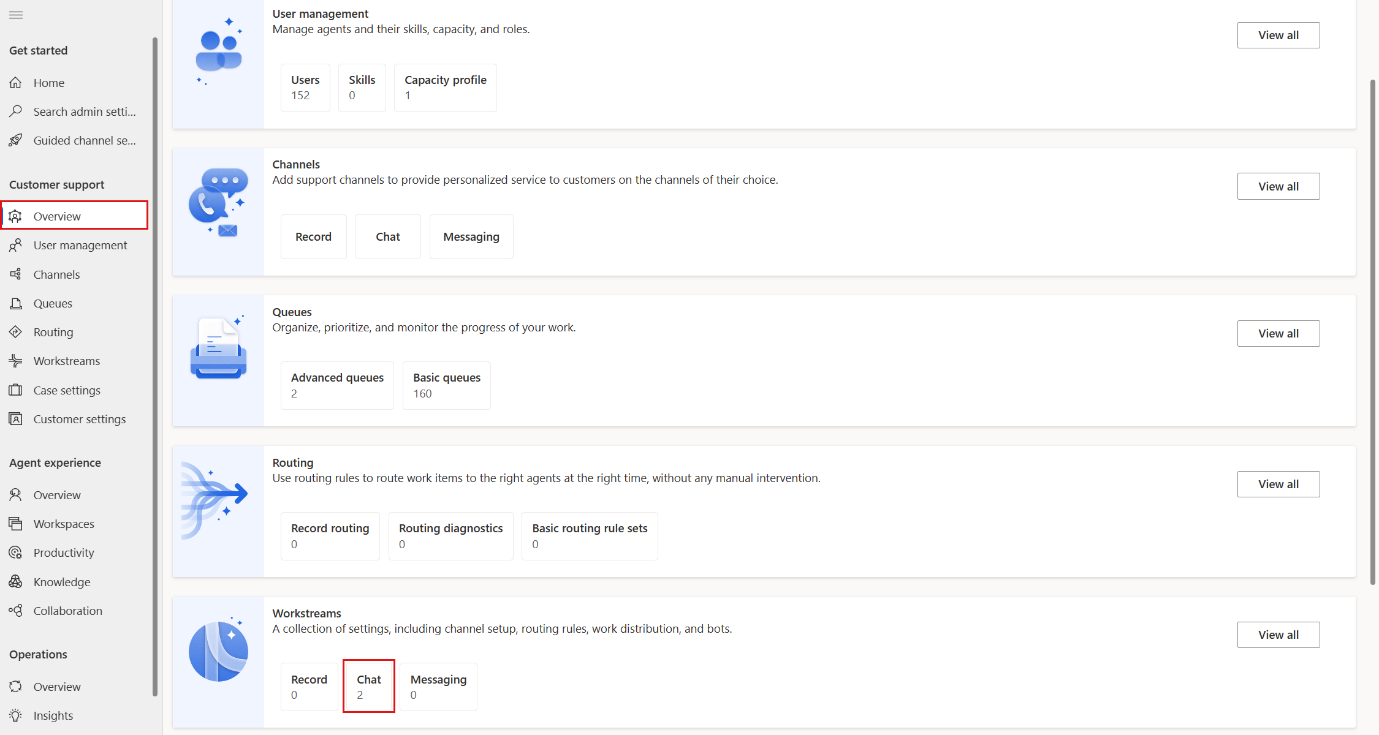
- Select Chat Workstream and then select Edit.
- In the Chat Workstream record, select Edit for the Fallback queue.
- Select the Default messaging queue(All users) from the Choose existing dropdown menu. Select Save and close.
- The updated fallback queue will display. Select + Add bot to add the Azure Health Bot for initial routing.
- Select your bot user from the Name dropdown menu. Select Connect.
- The bot user has been added. Now, you’ll need to edit the ruleset so that the queue properly escalates to a human agent. First, you’ll need a number variable to use with your escalation logic. On the lower-left corner of the Workstream page, select Show advanced settings.
- Review the advanced settings for the workstream and then select + Add context variable.
- In the Add context variable screen, select + Add. Create the new context variable, which you’ll use to determine whether you need to escalate to an agent or not. Enter EscalateToAgent as the Name and then select Number from the Type dropdown menu. Select Create.
- The EscalateToAgent context variable of the Number type should show as added. Close the Context variables screen.
- On the workstream record, select Show Advanced Settings to collapse it. Select Human Agent under Ruleset name.
- Select Human Agent Rule and then select Edit.
- Delete the initial condition in the rule to start with a blank canvas. The logic to follow is having the workstream route the chat channel to a human agent if the EscalateToHuman context variable is equal to 1 in any bot conversation.
- Select Add > Add related entity to add a new condition.
-
Select Context item value (Conversation) from the dropdown menu to have the routing rule check if conversation context values contain specific data.
-
After you select Context item value (Conversation), the following dropdown menu will populate with contains data and a sub condition will appear. Select the new EscalateToAgent context variable, and then set it as Equals to 1 in the condition. This setting will allow bot conversations to route to a human agent if that variable is ever set to 1. You’ll view this result in the last exercise in this module. Select Save and close.
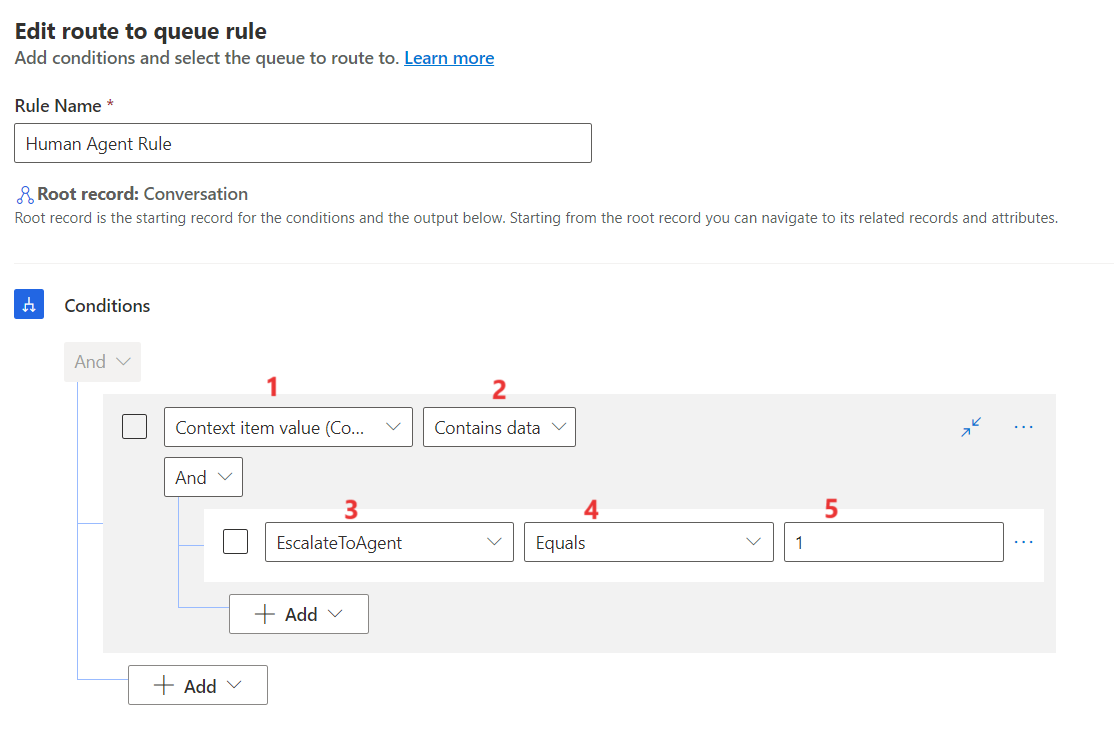
The Chat Workstream will show Human Agent Rule with the condition that will escalate to a human agent when the context variable is set to 1.
You’ve now created a new chat channel, workstream, queue, context variable, and routing rule that will allow customers to begin a conversation with a health bot and escalate to a human agent.
Embed Azure Health Bot in the Power Apps portal
In this exercise, you’ll embed the Omnichannel Chat Widget into the Power Apps Customer self-service portal by using the Portal Management configuration. In your environment, you created a Lamna Healthcare Company portal by using the Customer self-service portal template before deploying Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare.
Now, you’ll set up the chat widget to show on the customer website.
• Customer self-service portal – Enables customers to access self-service knowledge and support resources, view the progress of their cases, and provide feedback.
• Portal Management – Application to help you get started with the advanced portal configuration. In this exercise, you’ll learn how to set up the chat widget in the Portal Management app.
Follow these steps to complete the exercise:
- In Power Apps, select Apps in the left navigation pane and open the Portal Management app
- Select Content Snippets in the left navigation pane. Enter chat in the search box and then press the Enter key. Two Chat Widget Code records( Healthcare Patient Portal and the Lamna healthcare Patient portal you created) will be visible in the list as highlighted in the below screenshot.
- Select and edit each Chat Widget Code record, one at a time, to modify the Value contents with the chat widget code snippet that you previously saved. You can find the snippet in the Chat Workstream in the Customer Service admin center again if needed.
- In each Chat Widget Code record, under Value (HTML) paste the chat widget code snippet that you previously copied and saved. The Health Bot that you created is embedded in the Customer self-service portal and the Healthcare Patient Portal templates, whichever your portal website is currently set to show. Select Save & Close.
- Repeat the same step for the other chat widgets so that it will show on both website templates: the Healthcare Patient Portal and the one that’s associated with your current Customer self-service template.
- Test to ensure that the chat widgets are properly embedded. Go to Power Apps and select to open Lamna Healthcare Patient Portal
- The Azure Health Bot should display the Let’s Chat button in the lower-right corner of the screen. The chat widgets are successfully embedded into the Customer self-service portal.
- Test that the bot is properly connected. Go to your Health Bot management portal that you have created before from Azure Portal. Select Configuration > Conversation left navigation pane. Scroll down to the Automatic welcome section and enter a greeting for the portal user as Hello! This is a test. Select Save on the command bar.
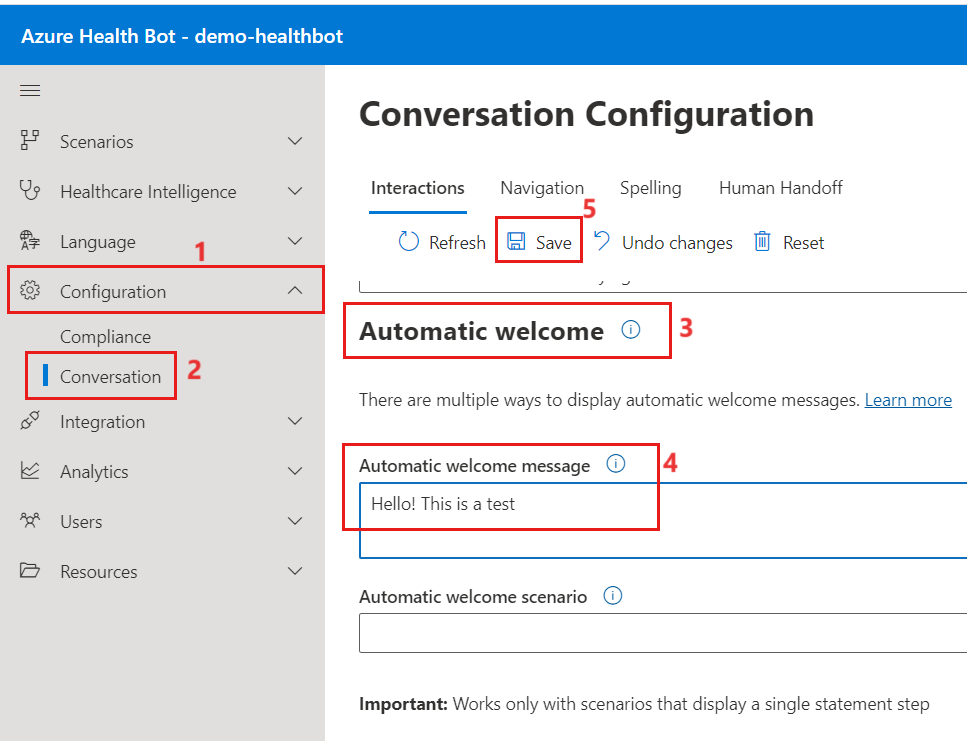
- Return to Lamna Healthcare Patient Portal with the Customer self-service template. Refresh the page and select the Let’s Chat widget, and the welcome message should greet you in the chat.
In this exercise, you’ve successfully updated the chat widget in the Power Apps portal content snippets. With this configuration, the Health Bot will be visible on the Power Apps portal for the Customer self-service template and the Healthcare Patient Portal template.
Extend Azure Health Bot with custom scenarios
Integration with Omnichannel for Dynamics 365 Customer Service allows the patient to interact with the Azure Health Bot by using the Dynamics 365 chat widget to access medical information and your custom scenarios. It also allows the escalation of a bot conversation to a live agent to continue the interaction. When a conversation is escalated, Dynamics passes along the conversation history and the context to the agent.
In this exercise, you’ll complete the following tasks:
-
Design the following Health Bot scenario called MCH_PatientService.
o Intro statement card - Triggers a welcome message to the customer.
o MedOrAgent card - Prompts with the Medication refill or Live Agent action authored card.
o IsMedRefill decision card - Checks the variable and submits a medication refill or starts live chat.
o Submit card - Prompts an adaptive card message (input text) with name, email, and medication name.
o Live Chat card - Communicates to the customer that they’re being directed to a live agent.
o Confirmation card - Repeats information that has been gathered from the submission and then thanks the customer.
o Escalate card - Triggers an escalate to live agent message on Omnichannel for Customer Service.
-
Design another Health Bot scenario called MCH_PatientServiceWelcome. This scenario holds the starting statement that will allow the user to invoke the MCH_PatientService scenario.
-
Set the Automatic Welcome Scenario to be the MCH_PatientServiceWelcome custom scenario that you create. This setting will begin the scenario when a user first interacts with the Health Bot.
Task: Create the MCH_PatientService scenario
In this task, you’ll create the MCH_PatientService bot scenario by using the designer canvas.
- Return to the Azure Health Bot instance home page where you set the bot settings. This link is the portal management link that you copied from the Azure portal. Select Create new scenario on the landing page. If you aren’t on the landing page, you can go to Scenario > Manage on the left navigation pane.
- Enter MCH_PatientService as the Name and the Scenario ID for the new Health Bot scenario.
- Design the scenario conversation, which should take you directly to the designer. If not, select the MCH_PatientService scenario in Scenarios > Manage to edit.
Step: Add a bot introduction statement
In this step, you’ll add a bot introduction statement.
- Click on the Plus(+) symbol.
- Add a beginning statement to the scenario by selecting the plus (+) sign in the center of the canvas and then by going to Conversational elements > Statement.
-
In the Display text box, enter the following message: Hi there, I’m your Healthcare Assistant.
-
Select the pencil icon next to Statement in the upper bar and change the Title to Intro. Select Save.
- The Intro statement will be added to the designer canvas. Double-click if you need to edit any item on the canvas.
Step: Add a statement for a medication request or a live agent
This section prompts two buttons: Medication Refill and Live Agent. When a user selects either button, the appropriate text to the MedicationOrAgent variable will be set.
- Add a prompt to the user by right clicking the canvas or by selecting Add element > Conversational elements > Prompt.
-
Enter the following details:
o Display text - Would you like to request a medication refill or chat with a live agent?
o Input variable - MedicationOrAgent
o Input type - String
o Title - Rename to MedOrAgent
- Scroll down and select the Add Cards button.
- Select Hero Card from the Card type dropdown menu. Leave the title blank because you’re already prompted with the display text. Select the plus (+) icon to add new actions so that the user can select a response to send to the bot.
-
Select the plus (+) icon twice to add two actions. For the first action, select the following values:
-
Action type - imBack
-
Action value - MedicationRefill
-
Action title - “Medication Refill”
-
-
For the second action, fill in the following values:
-
Action type - imBack
-
Action value - LiveAgent
-
Action title - “Live Agent”
-
-
Select OK to return to the prompt details. The Hero Card should be defined.
- Select Vertical from the Cards layout dropdown menu. Select Save.
- Move the Intro box above the MedOrAgent box and connect them. To do so, select the bottom circle on Intro and drag it to the top circle on the new prompt. An arrow automatically appears when you try to connect the Intro and MedOrAgent boxes. Select Save in the menu, which might have changed to an ellipsis (…).
- Remember to save often because the scenario won’t auto save. Now that the scenario has been saved, the run command should be enabled. Select Run from the menu to view the output in the Web Chat on the right.
The test welcome message should display from the previous exercise along with the new statement and prompt asking for a medication refill or chat with an agent.
Step: Add a MedicationOrAgent decision branch
This step checks whether the user has selected Medication Refill or Live Agent with the help of the MedicationOrAgent variable. It will redirect the message according to the selection.
- Right-click the canvas to bring up the menu, select Flow control elements > Branch to allow your logic to proceed in two different directions.
-
Enter the following expression in the Javascript Boolean expression box: scenario.MedicationOrAgent === “MedicationRefill”
-
Rename the branch to IsMedRefill and then select Save.
- Place the IsMedRefill below MedOrAgent. Select and drag the bottom circle of the MedOrAgent prompt to the top circle of the IsMedRefill branch decision to connect them.
Step: Prompt the user to enter data for the medication refill option
Your next step is to prompt the user to enter data for the medication refill option by following these steps:
- Add a Prompt element that will be used to display the form data (by using an Adaptive Card) to capture the patient’s name, email, and phone number to create an appointment.
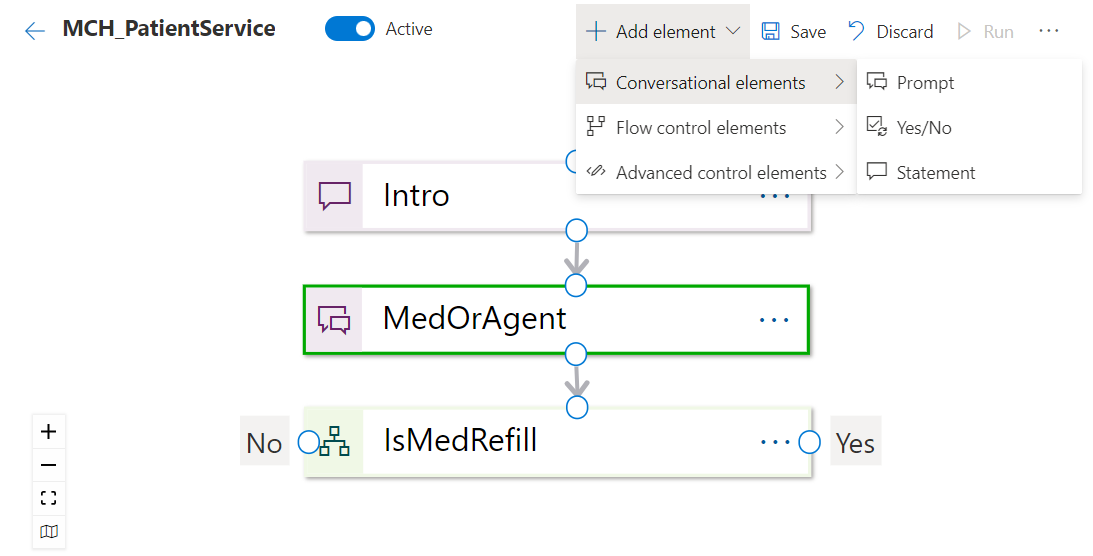
-
Add the following details. When you’re finished, select the Add Cards button.
o Input variable - formData
o Input type - Object
o Title - Submit
- Change the Card type to Adaptive Card. Add the following JSON to your card to show multiple fields of input for the user in an appealing format. Select OK.
JSON for adaptive card:
{
“$schema”: “http://adaptivecards.io/schemas/adaptive-card.json”,
“type”: “AdaptiveCard”,
“version”: “1.0”,
“body”: [
{
“type”: “ColumnSet”,
“columns”: [
{
“type”: “Column”,
“width”: 2,
“items”: [
{
“type”: “TextBlock”,
“text”: “Tell us about yourself”,
“weight”: “bolder”,
“size”: “medium”
},
{
“type”: “TextBlock”,
“text”: “We just need a few more details to get your Medication refill.”,
“isSubtle”: true,
“wrap”: true
},
{
“type”: “TextBlock”,
“text”: “Don’t worry, we’ll never share or sell your information.”,
“isSubtle”: true,
“wrap”: true,
“size”: “small”
},
{
“type”: “TextBlock”,
“text”: “Your name”,
“wrap”: true
},
{
“type”: “Input.Text”,
“id”: “myName”,
“placeholder”: “Full name”
},
{
“type”: “TextBlock”,
“text”: “Your email”,
“wrap”: true
},
{
“type”: “Input.Text”,
“id”: “myEmail”,
“placeholder”: “youremail@example.com”,
“style”: “email”
},
{
“type”: “TextBlock”,
“text”: “Medication Requested”
},
{
“type”: “Input.Text”,
“id”: “myMedReq”,
“placeholder”: “Medication Name”,
“wrap”: “true”
}
]
}
]
} ],
“actions”: [
{
“type”: “Action.Submit”,
“title”: “Submit”
} ]
}
Note - Go to the Adaptive Card visualizer to test your own authored card.
- On the prompt form, select Vertical from the Cards layout dropdown menu. Select Save.
- Connect the Yes condition of the IsMedRefill branch to the Submit prompt.
- Save and Run your current scenario. If you don’t save the scenario first, it won’t run with updates that have been made since the last save. If you haven’t saved at all, it won’t recognize any conversation.
The Adaptive Card output should display in the Web Chat when the system is running the conversation and selecting Medication Refill when prompted.
Step: Add a confirmation statement
To add a confirmation statement, follow these steps:
- Add a Statement element.
-
Set the Display text as follows:
scenario.formData.myName + “ - Thanks for providing the information, we have created a Medication Request for you regarding the following medication: “ + scenario.formData.myMedReq
-
Rename the statement to Confirmation and then select Save.
- Connect the Submit element to the Confirmation element on the designer canvas.
-
Select Save and Run to view your scenario in the web chat. Select Refill Medication in the authored card.
-
Fill in information for the request and then select Submit. Note the confirmation text that’s returned from the bot, which was defined in your confirmation step.
Step: Invoke a live agent action
To invoke a live agent action, follow these steps:
-
Add a Statement element to the canvas.
-
In the Display text box, enter Please wait, I am transferring your request to a live agent for further assistance.
-
Rename the statement to Live Chat and then select Save.
- Connect the No decision of the IsMedRefill branch to the Live Chat statement.
Step: Add an action to invoke escalation
To add an action to invoke escalation, follow these steps:
- Add an Action element to the canvas under Advanced control elements, which you’ll use to trigger an escalation to an Omnichannel live agent.
-
Add the following code to the action, which will trigger the live agent chat:
session.sendChannelData(‘Escalating…’, { “tags”: JSON.stringify({type: “Escalate”, context: {“EscalateToAgent”: 1}}) });
-
Name the action Escalate and then select Save to return to the designer page.
Connect the Live Chat statement to the new Escalate action.
You’ve now completed the final connection. The following screenshot shows your full scenario.
-
Save and Run your scenario to view the full scenario output.
-
Select Live Agent in the authored card to show the escalation action.
- Exit the MCH_PatientService scenario editor with the back arrow next to your scenario name. Make sure that you save before confirming to exit.
You’ve now created a custom scenario to allow the patient to refill a medication or escalate to a live agent.
Task: Create the MCH_PatientServiceWelcome scenario
In this task, you’ll create another bot scenario called MCH_PatientServiceWelcome to invoke the MCH_PatientService scenario. Because the automatic welcome message in the Health Bot settings can be only one step, you’ll use it to initiate the multi-step scenario that you created.
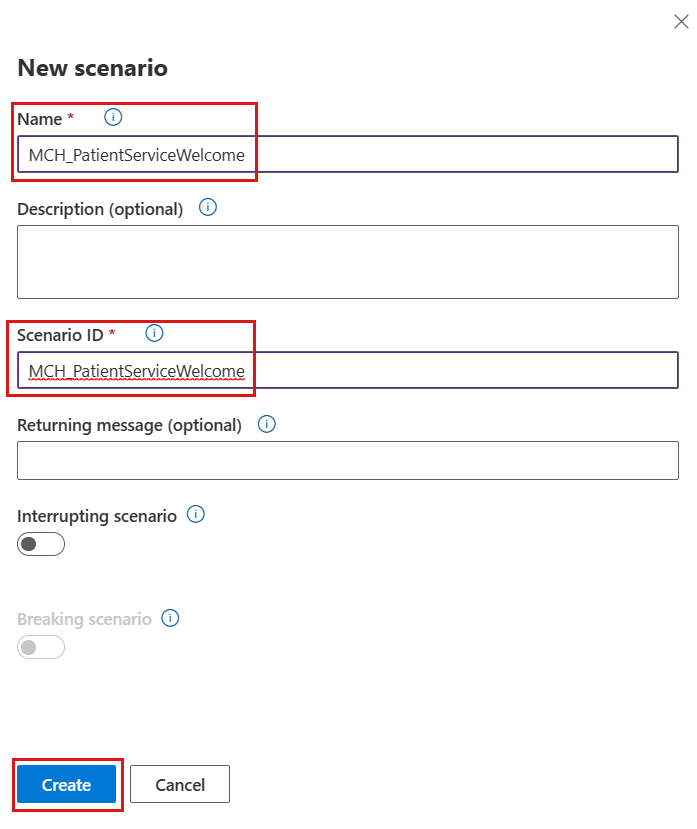
- On the Azure Health Bot scenarios page, select New to create another new scenario.
- Enter MCH_PatientServiceWelcome as the Name and the Scenario ID for the new Health Bot scenario. Select Create.
- On the scenario editor designer, add a Statement element.
- Rename the statement to Welcome. Add a Display text as – Welcome to Lamna Healthcare Patient Service Portal. Select Add Cards.
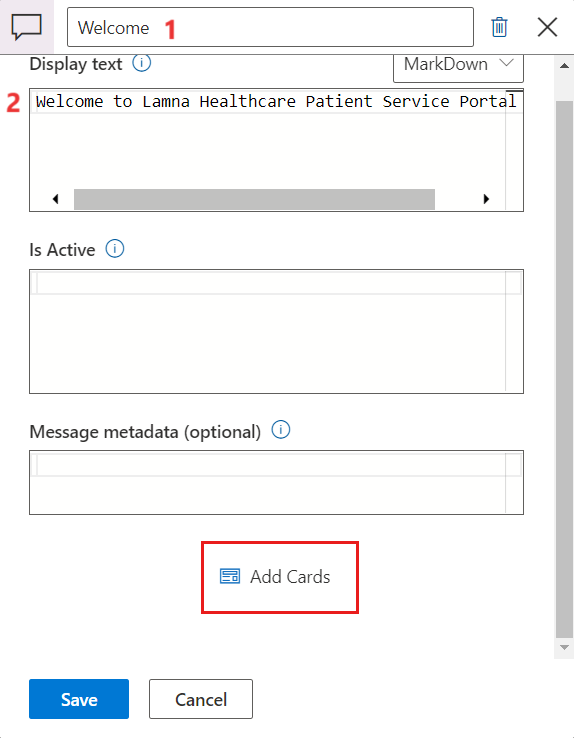
- Select Hero Card from the Card type dropdown menu. Select the plus (+) icon to add an action.
-
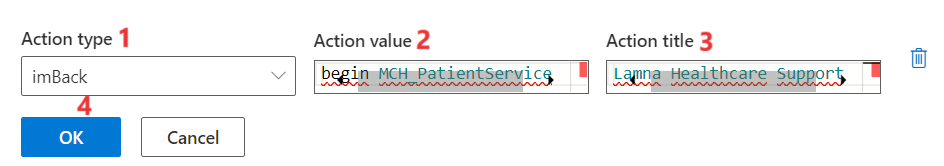
Provide the following details for the action:
o Action type - imBack
o Action value - begin MCH_PatientService
o Action title - “Lamna Healthcare Support”
- Select OK and then select Save on the statement form.
- Save and Run to test your MCH_PatientServiceWelcome bot scenario in the Web Chat.
- Exit the scenario designer.
You’ve now created a welcome scenario that will kick off the MCH_PatientService scenario.
Task: Set up the welcome scenario to be automatic
In this task, you’ll set the MCH_PatientServiceWelcome to be the Automatic Welcome Scenario in settings. This setting will always trigger the scenario when a user starts a conversion with the Health Bot from the portal.
- Go to Configuration > Conversation from the left navigation pane.
- On the Interactions tab, scroll down to the Automatic welcome section. From the Automatic welcome scenario dropdown menu, select the MCH_ PatientServiceWelcome scenario. You can clear the automatic welcome message that you previously set. Select Save.
You’ve successfully set the MCH_PatientServiceWelcome scenario as the default scenario that kicks off when a user interacts with the Health Bot.
Task: Test Health Bot escalation from Power Apps portal to Omnichannel
In this task, you’ll test the escalation experience from the Power Apps portal to an Omnichannel live agent.
-
Go to Power Apps. Select the correct environment and open Lamna Healthcare Patient Portal.
-
The Azure Health Bot Let’s Chat button should display in the lower-right corner of the screen, meaning that the chat widget was successfully embedded into the Customer self-service portal.
- When you select the chat widget, the bot will trigger the welcome scenario message that you created and will set it as the default welcome message, MCH_PatientServiceWelcome.
- Return to Power Apps and open Customer Service workspace.
Note - Escalation into the Customer Service workspace will work only when the Presence status shows as enabled. A splash loading screen will show that goes through multiple steps and then displays the status indicator as Available after it’s loaded. The status is enabled when it shows a check mark in a green circle.
- In the Health Bot dialog in the Patient Portal, select the Healthcare Support button and then select the Live Agent button to witness the escalation into Omnichannel to chat with a live agent (you).
-
Return to Omnichannel for Customer Service. Your user, as the Live Agent, should receive an incoming notification with Accept and Reject options for the chat.
-
Select Accept to connect and chat with the customer, or in this case, the patient.
- When a live chat agent accepts the incoming chat notification, Omnichannel for Customer Service will open a Live Chat widget, where the agent can view the entire bot conversation with the user and continue to chat with them.
Now, you’ve successfully tested the escalation scenario from the patient by using a Health Bot in the Power Apps portal to a live agent in Omnichannel for Customer Service.













































































































