Explore real-time analytics in Microsoft Fabric
Microsoft Fabric provides Real-Time Intelligence, enabling you to create analytical solutions for real-time data streams. In this exercise, you’ll use the Real-Time Intelligence capabilities in Microsoft Fabric to ingest, analyze, and visualize a real-time stream of data from a taxi company.
This lab takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Note: You need a Microsoft Fabric tenant to complete this exercise.
Create a workspace
Before working with data in Fabric, you need to create a workspace with the Fabric capacity enabled.
Tip: A workspace is the container for everything you create (eventstreams, eventhouses, dashboards). Fabric capacity lets these items run.
-
Navigate to the Microsoft Fabric home page at
https://app.fabric.microsoft.com/home?experience=fabricin a browser, and sign in with your Fabric credentials. -
In the menu bar on the left, select Workspaces (the icon looks similar to 🗇).
-
Create a new workspace with a name of your choice, selecting a licensing mode that includes Fabric capacity (Trial, Premium, or Fabric).
Tip: Using a capacity that includes Fabric ensures the workspace has the engines needed for real-time ingestion and analytics. A separate workspace keeps lab resources isolated and easy to clean up.
-
When your new workspace opens, it should be empty.
Create an eventstream
Now you’re ready to find and ingest real-time data from a streaming source. To do this, you’ll start in the Fabric Real-Time Hub.
Tip: The Real-Time Hub centralizes streaming sources and makes it easy to connect them. An eventstream stitches sources to destinations and can add transformations in between.
Tip: The first time you use the Real-Time Hub, some getting started tips may be displayed. You can close these.
-
In the menu bar on the left, select the Real-Time hub.
The real-time hub provides an easy way to find and manage sources of streaming data.
-
In the real-time hub, in the Connect to section, select Data sources.
-
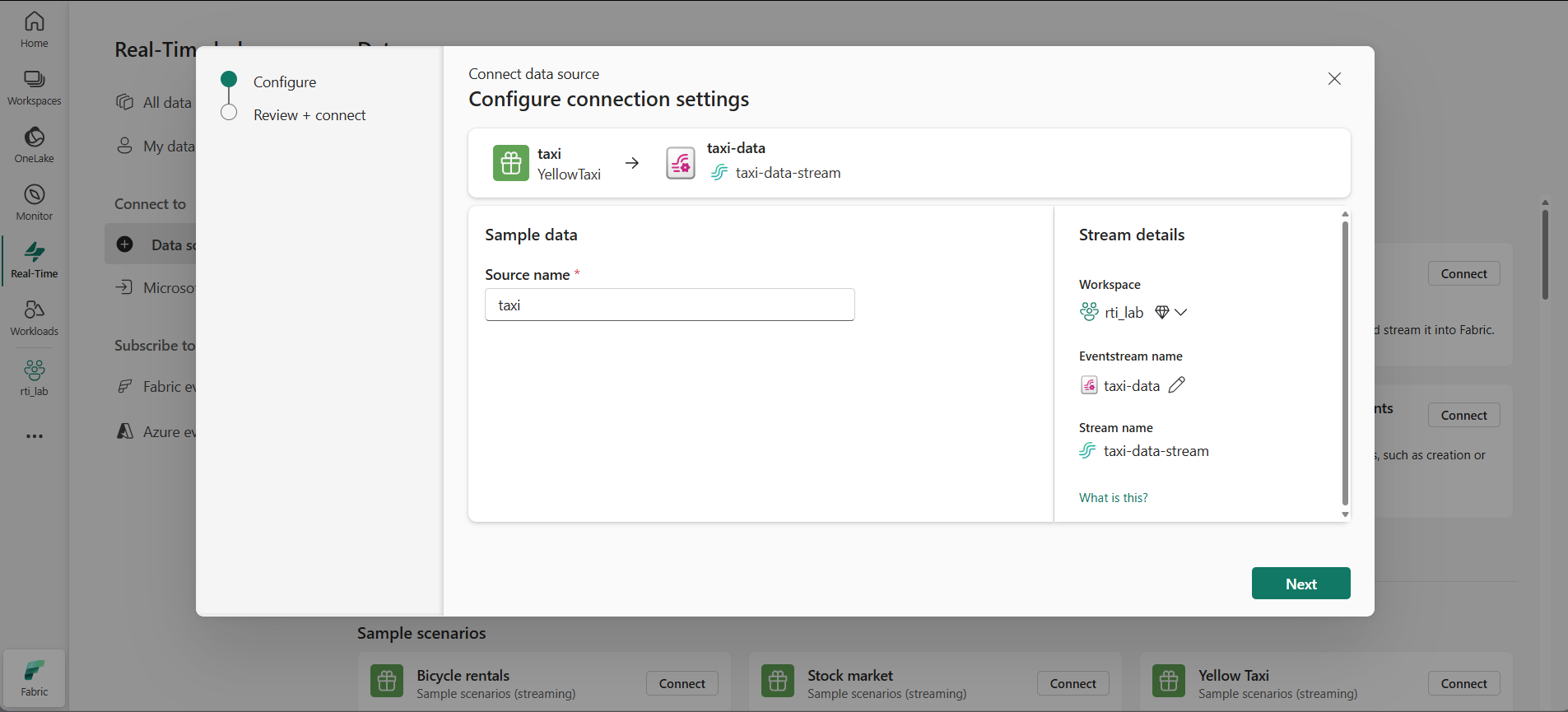
Find the Yellow taxi sample data source and select Connect. Then in the Connect wizard, name the source
taxiand edit the default eventstream name to change it totaxi-data. The default stream associated with this data will automatically be named taxi-data-stream:Tip: The Yellow taxi sample is a safe, public stream—no credentials required—and it’s consistent for all learners. Clear names make it easier to find your source, eventstream, and stream later.
-
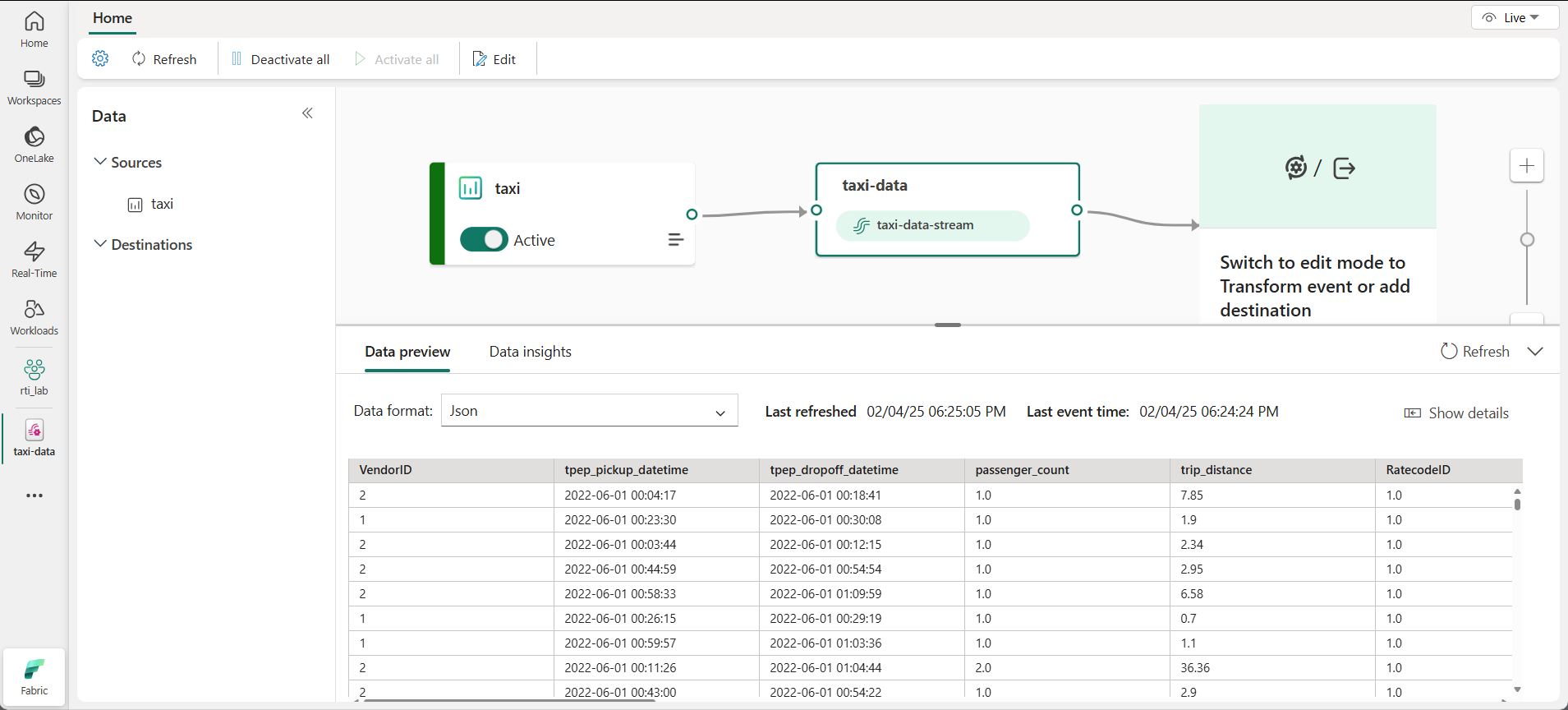
Select Next and wait for the source and eventstream to be created, then select Open eventstream. The eventstream will show the taxi source and the taxi-data-stream on the design canvas:
Create an eventhouse
The eventstream ingests the real-time taxi data, but doesn’t currently do anything with it. Let’s create an eventhouse where we can store the captured data in a table.
Tip: An eventhouse gives you durable storage and a KQL database so you can persist the stream and query it later—even as new events arrive. KQL (Kusto Query Language) is a read-only, SQL-like language used to quickly explore, filter, and analyze large datasets
-
On the menu bar on the left, select Create. In the New page, under the Real-Time Intelligence section, select Eventhouse. Give it a unique name of your choice.
Note: If the Create option is not pinned to the sidebar, you need to select the ellipsis (…) option first.
Close any tips or prompts that are displayed until you see your new empty eventhouse.
-
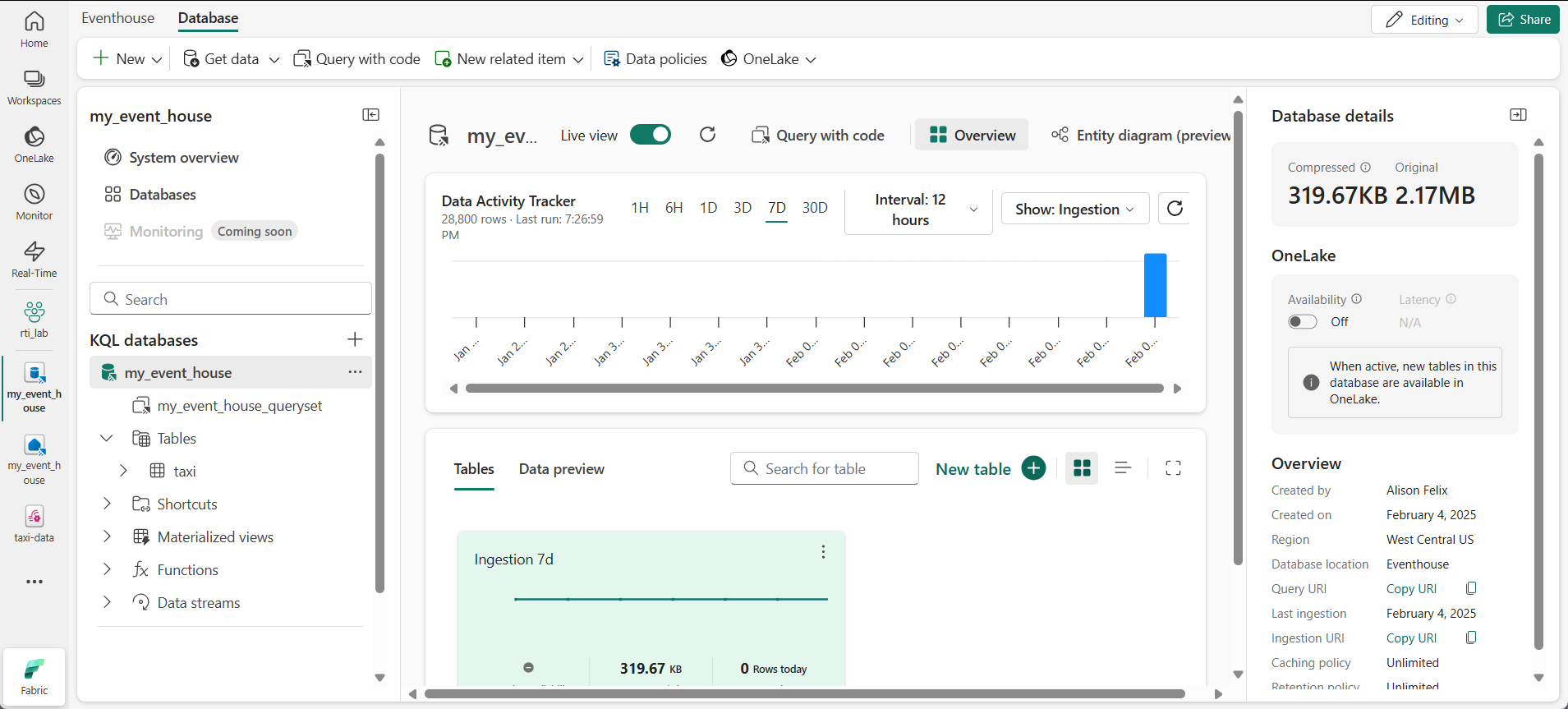
In the pane on the left, note that your eventhouse contains a KQL database with the same name as the eventhouse. You can create tables for your real-time data in this database, or create additional databases as necessary.
-
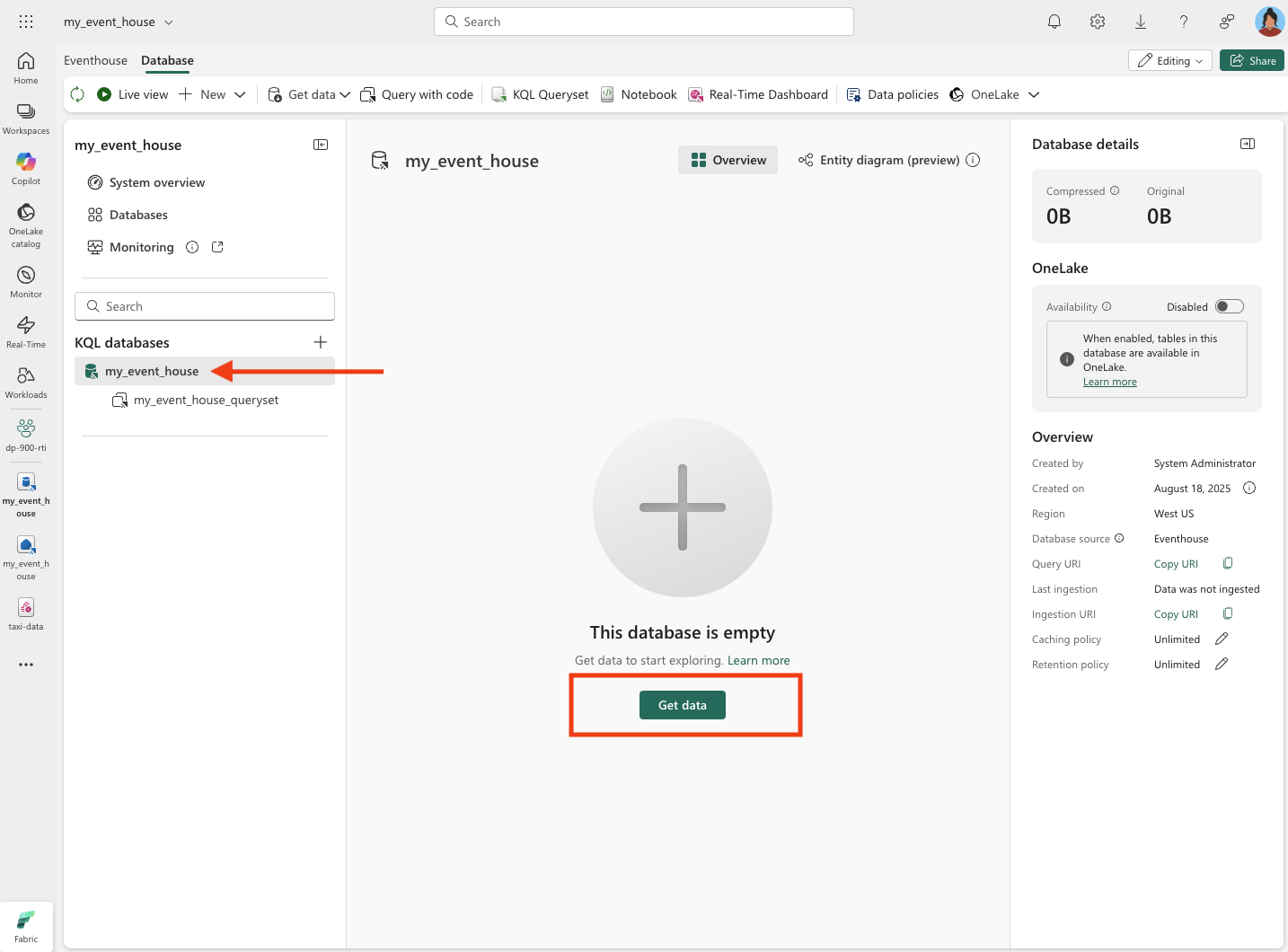
Select the database, and note that there is an associated queryset. This file contains some sample KQL queries that you can use to get started querying the tables in your database.
Tip: The KQL database holds your tables. The queryset is a handy place to write and run queries without extra setup.
However, currently there are no tables to query. Let’s resolve that problem by getting data from the eventstream into a new table.
-
In the main page of your KQL database, select Get data.
-
For the data source, select Eventstream > Existing eventstream.
-
In the Select or create a destination table pane, create a new table named
taxi. Then in the Configure the data source pane, select your workspace and the taxi-data eventstream and name the connectiontaxi-table.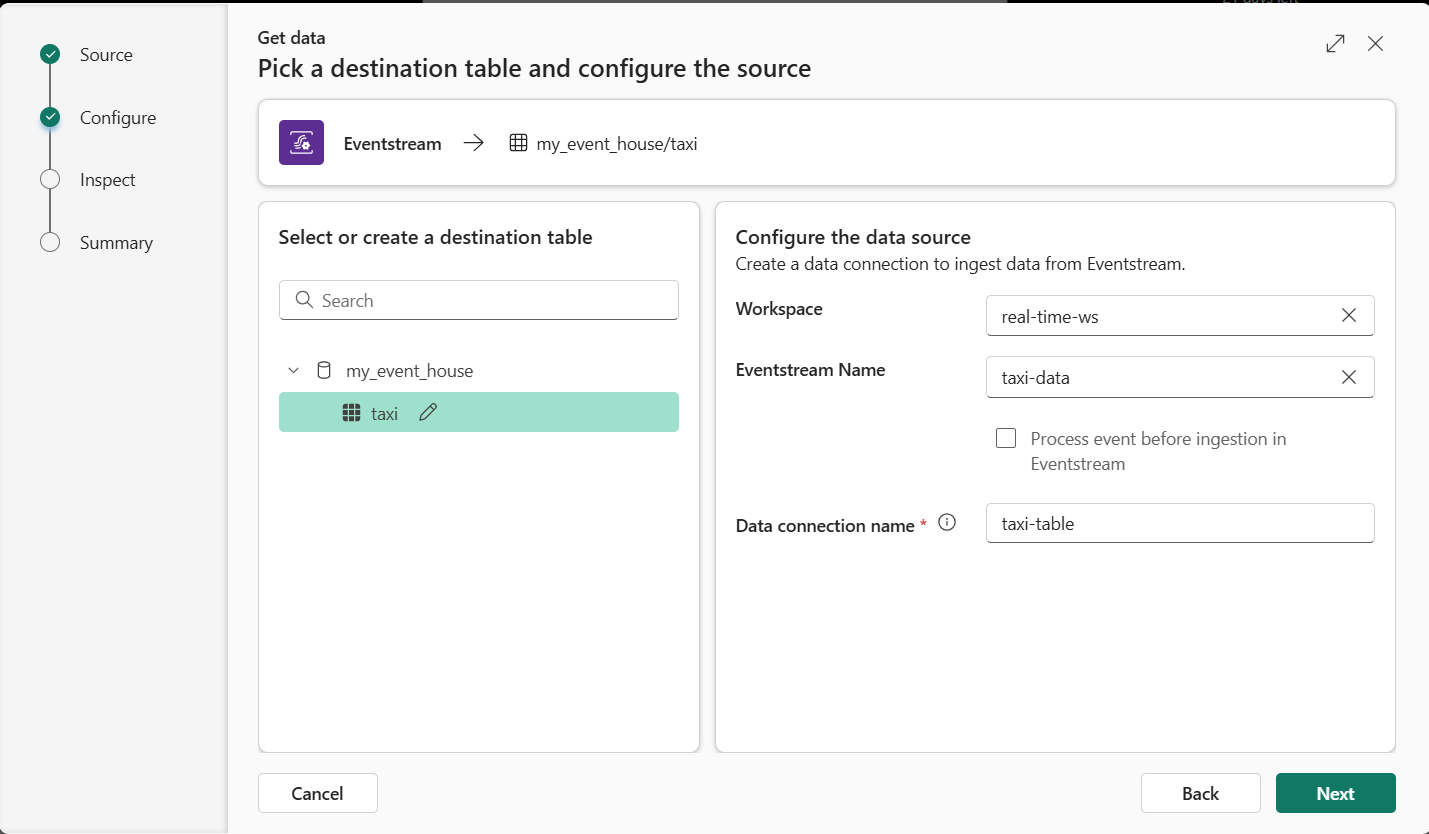
-
Use the Next button to complete the steps to inspect the data and then finish the configuration. Then close the configuration window to see your eventhouse with the taxi table.
The connection between the stream and the table has been created. Let’s verify that in the eventstream.
-
In the menu bar on the left, select the Real-Time hub and then view the My data streams page. In the … menu for the taxi-data-stream stream, select Open eventstream.
The eventstream now shows a destination for the stream:
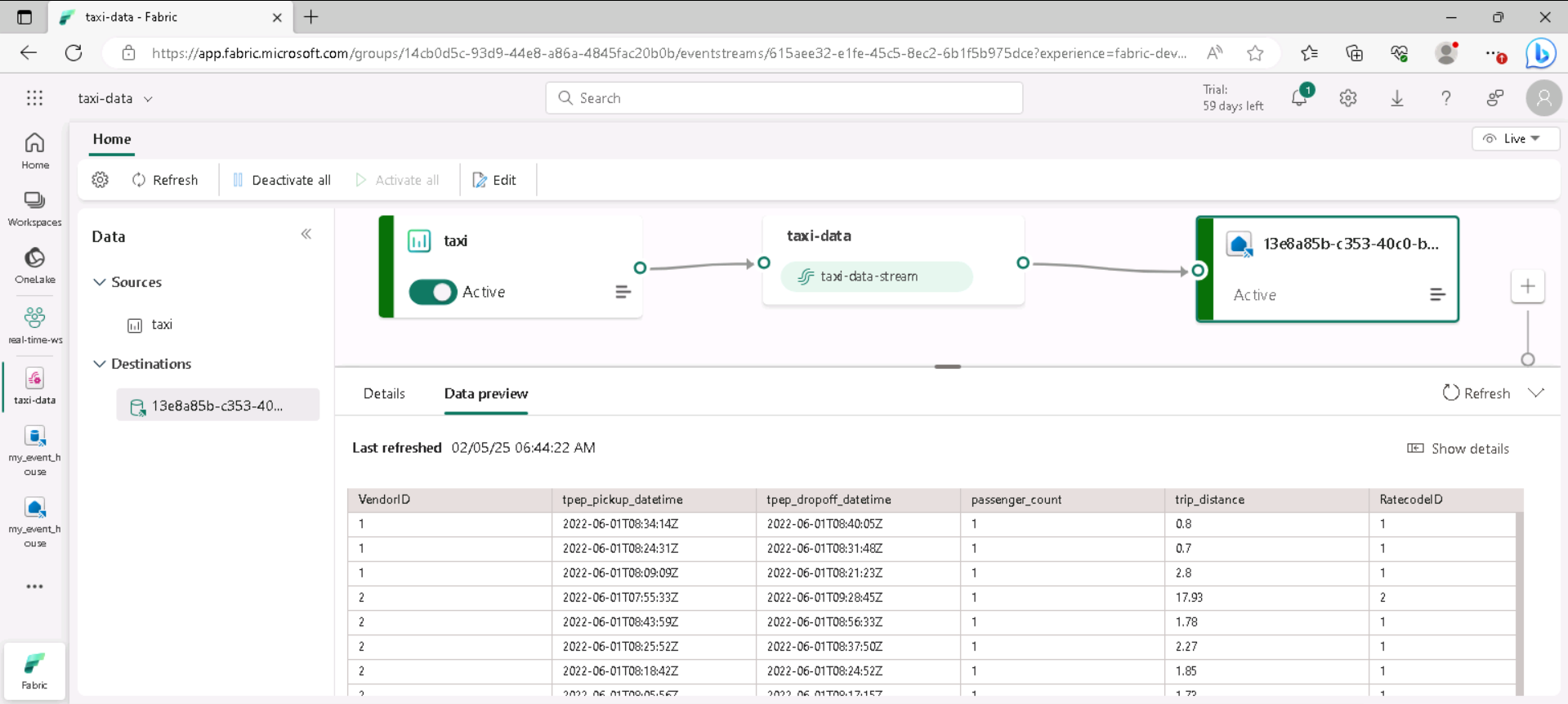
Tip: Select the destination on the design canvas, and if no data preview is shown beneath it, select Refresh.
Tip: Verifying in the eventstream confirms events are flowing to the destination. The preview may cache — refresh pulls the latest sample.
In this exercise, you’ve created a very simple eventstream that captures real-time data and loads it into a table. In a real solution, you’d typically add transformations to aggregate the data over temporal windows (for example, to capture the average price of each stock over five-minute periods).
Now let’s explore how you can query and analyze the captured data.
Query the captured data
The eventstream captures real-time taxi fare data and loads it into a table in your KQL database. You can query this table to see the captured data.
Tip: KQL is designed for fast exploration of time-stamped, high-volume data. Querying lets you validate ingestion and start analysis immediately.
-
In the menu bar on the left, select your eventhouse database.
-
Select the queryset for your database.
-
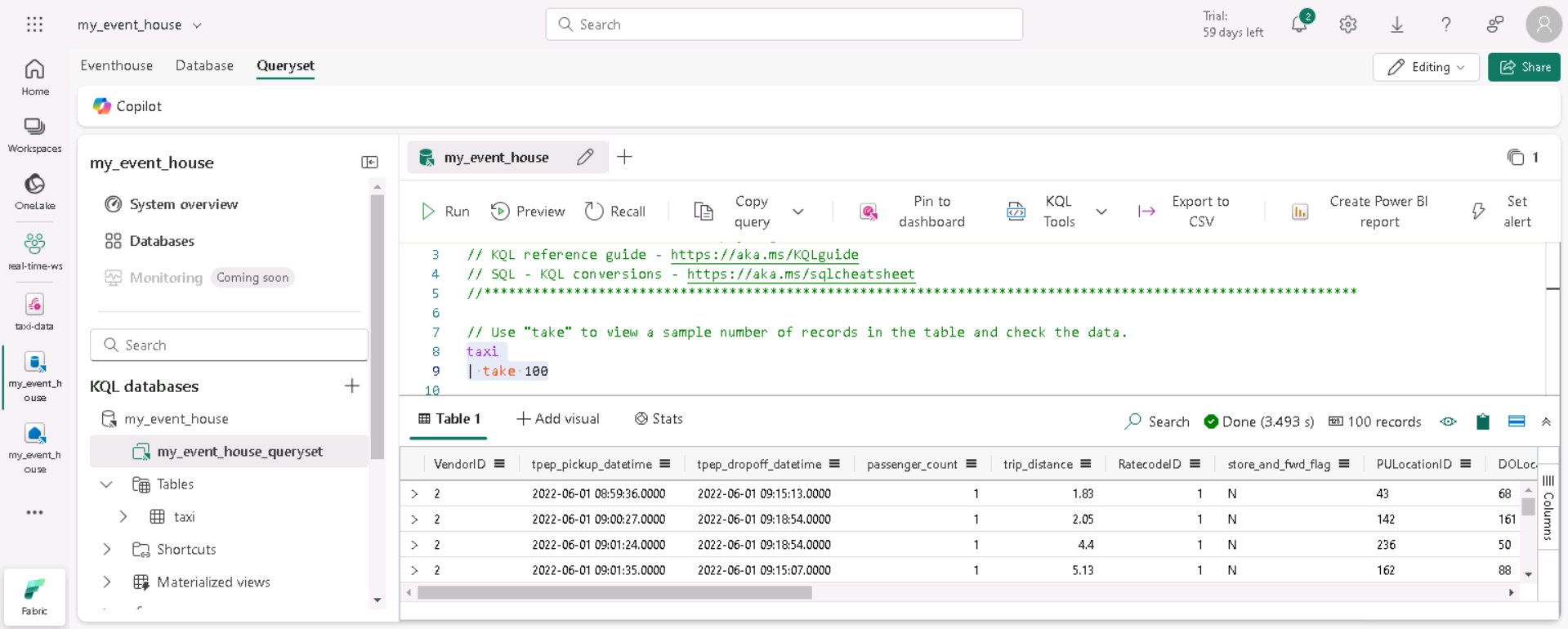
In the query pane, modify the first example query as shown here:
taxi | take 100Tip:
take 100is a quick health check—confirm rows are arriving and inspect a small sample without scanning everything. -
Select the query code and run it to see 100 rows of data from the table.
-
Review the results, then modify the query to show the number of taxi pickups for each hour:
taxi | summarize PickupCount = count() by bin(todatetime(tpep_pickup_datetime), 1h) -
Highlight the modified query and run it to see the results.
Tip:
bin(..., 1h)groups events into hourly buckets, making it easy to spot trends over time. -
Wait a few seconds and run it again, noting that the number of pickups change as new data is added to the table from the real-time stream.
Tip: The stream keeps adding data, so results change over time. Re-running shows how aggregations update as fresh events arrive.
Clean up resources
In this exercise, you have create an eventhouse, ingested real-time data using an eventstream, queried the ingested data in a KQL database table, created a real-time dashboard to visualize the real-time data, and configured an alert using Activator.
If you’ve finished exploring Real-Time Intelligence in Fabric, you can delete the workspace you created for this exercise.
Tip: Deleting the workspace removes all items created in the lab and helps prevent ongoing charges.
-
In the bar on the left, select the icon for your workspace.
-
In the toolbar, select Workspace settings.
-
In the General section, select Remove this workspace.