Explore Azure Cosmos DB
By completing this lab, you’ll learn how to provision an Azure Cosmos DB account, create a sample database and container, add and view JSON items, and run SQL-like queries to retrieve data. You’ll gain hands-on experience with the Azure portal and understand how Cosmos DB supports flexible, non-relational data storage and querying.
This lab will take approximately 15 minutes to complete.
Before you start
You’ll need an Azure subscription in which you have administrative-level access.
Create a Cosmos DB account
To use Cosmos DB, you must provision a Cosmos DB account in your Azure subscription. In this exercise, you’ll provision a Cosmos DB account that uses Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL.
-
In the Azure portal, select + Create a resource at the top left, and search for
Azure Cosmos DB. In the results, select Azure Cosmos DB and select Create.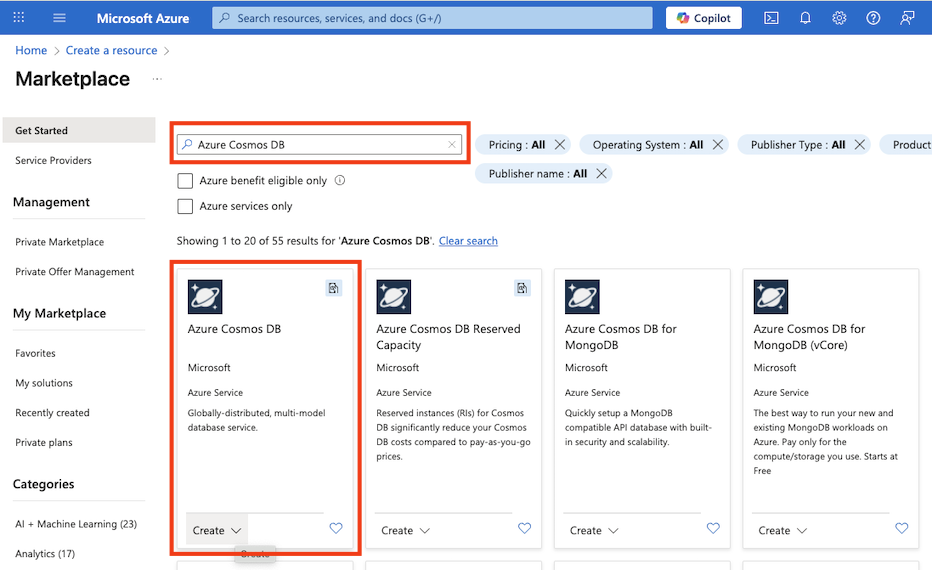
-
In the Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL tile, select Create.
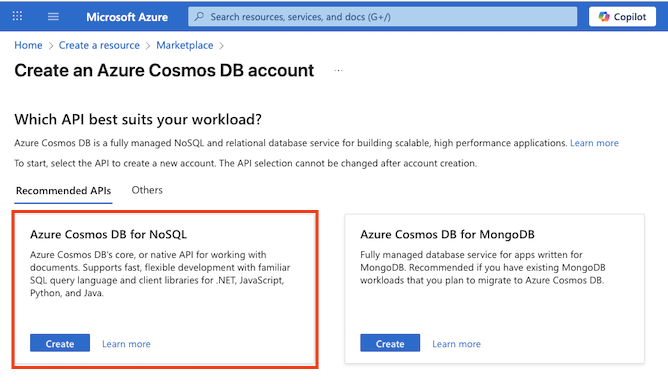
Tip: The account is the top level for your Cosmos DB resources. Choosing Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL lets you store and query JSON data with a simple, SQL-like query language.
-
Enter the following details, and then select Review + Create:
- Workload Type: Learning
- Subscription: If you’re using a sandbox, select Concierge Subscription. Otherwise, select your Azure subscription.
- Resource group: If you’re using a sandbox, select the existing resource group (which will have a name like learn-xxxx…). Otherwise, create a new resource group with a name of your choice.
- Account Name: Enter a unique name
- Availability Zones: Disable
- Location: Choose any recommended location
- Capacity mode: Provisioned throughput
- Apply Free-Tier Discount: Select Apply if available
- Limit total account throughput: Unselected
Why these choices?
We’re setting the workload type to Learning because it comes with beginner-friendly defaults that make setup easier and keep costs low. Your account name needs to be unique across the whole service, since it becomes part of your service’s URL. We’re picking a location close to you so your tests run faster; which locations you see will depend on your subscription and whether certain availability zones are enabled. For capacity mode, we’re going with Provisioned throughput so performance stays predictable during this short lab—though Serverless can be fine if you only need it occasionally. If the free tier is available, we’ll use it so you can experiment without racking up charges. Finally, we’re keeping the “limit total account throughput” setting turned off so nothing gets slowed down unexpectedly while you work.
-
When the configuration has been validated, select Create.
Tip: Azure Portal will estimate how long it will take to provision this instance of CosmosDB. The estimated creation time is calculated based on the location you have selected.
-
Wait for deployment to complete. Then go to the deployed resource.
Create a sample database
Throughout this procedure, close any tips that are displayed in the portal.
-
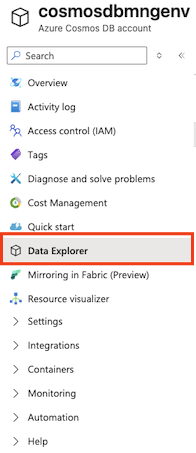
On the page for your new Cosmos DB account, in the pane on the left, select Data Explorer.
-
In the Data Explorer page, select Launch quick start.
Tip: Quick start creates a working database, container, and sample data so you can practice adding and querying items without designing a schema first.
-
In the New container tab, review the pre-populated settings for the sample database, and then select OK.
-
Observe the status in the panel at the bottom of the screen until the SampleDB database and its SampleContainer container has been created (which may take a minute or so).
View and create items
-
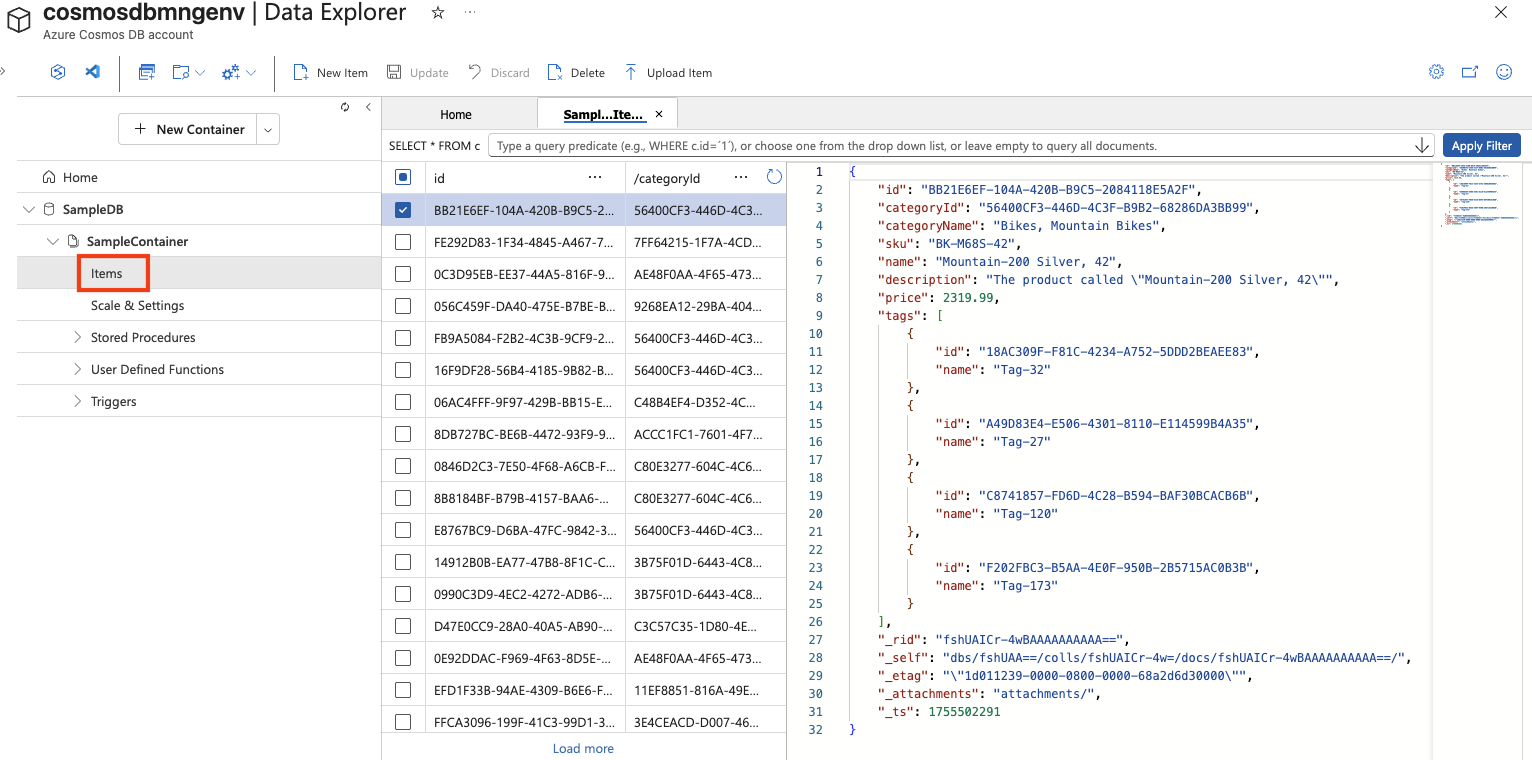
In the Data Explorer page, expand the SampleDB database and the SampleContainer container, and select Items to see a list of items in the container. The items represent product data, each with a unique id and other properties.
-
Select any of the items in the list to see a JSON representation of the item data.
-
At the top of the page, select New Item to create a new blank item.
-
Modify the JSON for the new item as follows, and then select Save.
{ "name": "Road Helmet,45", "id": "123456789", "categoryID": "123456789", "SKU": "AB-1234-56", "description": "The product called \"Road Helmet,45\" ", "price": 48.74 }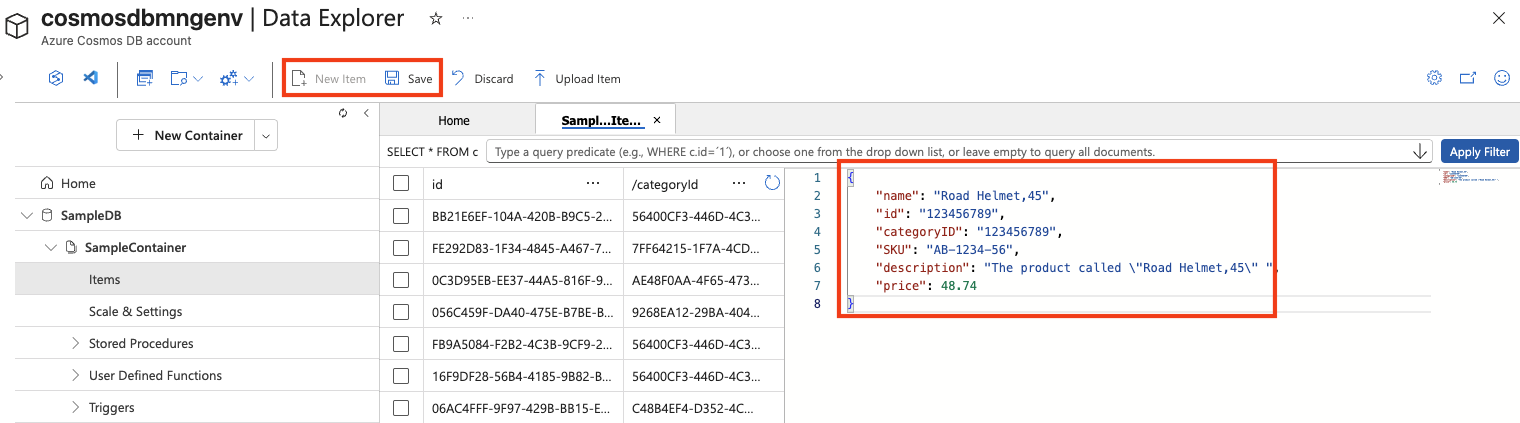
-
After saving the new item, notice that additional metadata properties are added automatically.
Tip: Cosmos DB stores items as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), so you can add fields that fit your scenario without a rigid schema. The
idmust be unique within the container. After you save, Cosmos DB adds system properties (like timestamps and internal identifiers) to help manage and optimize your data:- _rid — The internal resource ID used by Cosmos DB to identify the item internally.
- _self — The full resource link for the item.
- _etag — The entity tag used for optimistic concurrency checks.
- _ts — The Unix timestamp (in seconds) when the item was last modified.
- _attachments — A link to the document’s attachments (if any).
Query the database
-
In the Data Explorer page, select the New SQL Query icon.

-
In the SQL Query editor, review the default query (
SELECT * FROM c) and use the Execute Query button to run it. -
Review the results, which includes the full JSON representation of all items.
-
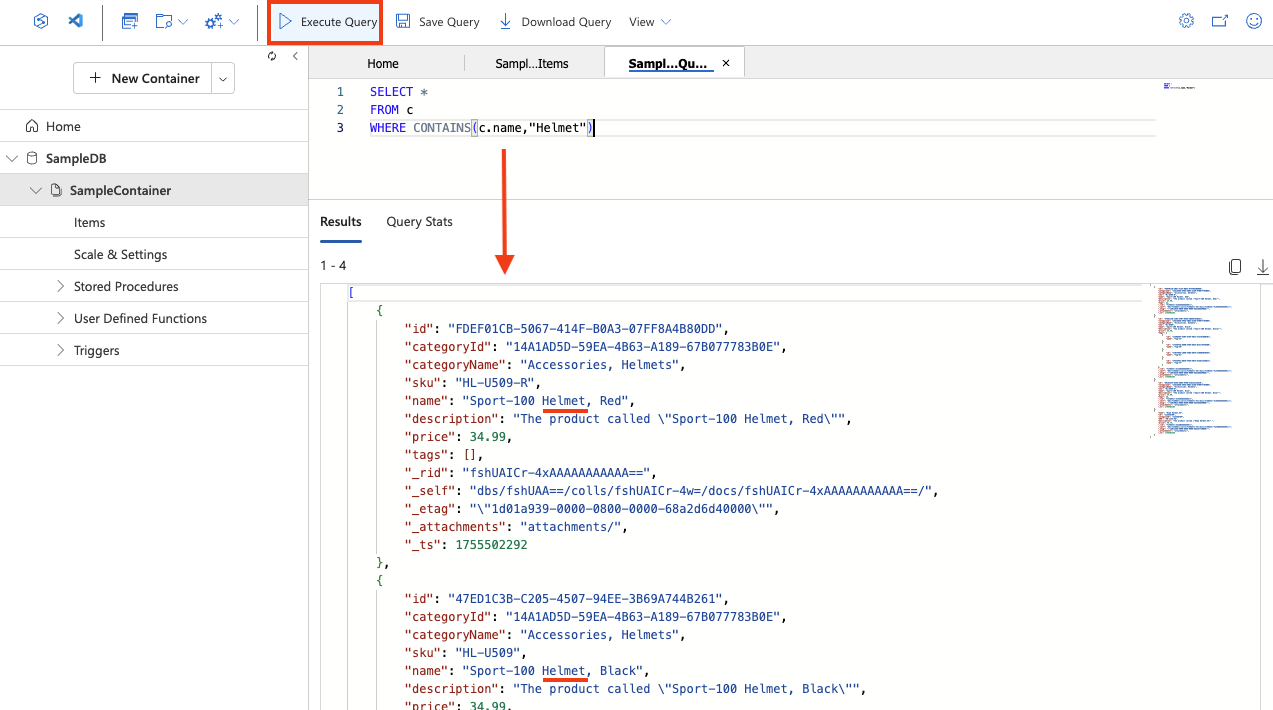
Modify the query as follows:
SELECT * FROM c WHERE CONTAINS(c.name,"Helmet")Tip: The NoSQL API uses familiar, SQL-like queries to search JSON documents.
SELECT * FROM clists all items, andCONTAINSfilters by text inside a property—useful for quick searches without extra setup. -
Use the Execute Query button to run the revised query and review the results, which includes JSON entities for any items with a name field containing the text “Helmet”.
-
Close the SQL Query editor, discarding your changes.
You’ve seen how to create and query JSON entities in a Cosmos DB database by using the data explorer interface in the Azure portal. In a real scenario, an application developer would use one of the many programming language specific software development kits (SDKs) to call the NoSQL API and work with data in the database.
Tip: If you’ve finished exploring Azure Cosmos DB, you can delete the resource group that you created in this exercise.