Explore Azure Storage
In this exercise, you’ll learn how to provision and configure an Azure Storage account, and explore its core services: Blob storage, Data Lake Storage Gen2, Azure Files, and Azure Tables. You’ll gain hands-on experience with creating containers, uploading data, enabling hierarchical namespaces, setting up file shares, and managing table entities. These skills will help you understand how to store, organize, and secure non-relational data in Azure for various analytics and application scenarios.
This lab will take approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Tip: Understanding the purpose of each action helps you later design storage solutions that balance cost, performance, security, and analytics goals. These brief Why notes tie each step to a real-world reason.
Before you start
You’ll need an Azure subscription in which you have administrative-level access.
Provision an Azure Storage account
The first step in using Azure Storage is to provision an Azure Storage account in your Azure subscription.
Tip: A storage account is the secure, billable boundary for all Azure Storage services (blobs, files, queues, tables). Policies, redundancy, encryption, networking, and access control apply from here downward.
-
If you haven’t already done so, sign into the Azure portal.
-
On the Azure portal home page, select + Create a resource from the upper left-hand corner and search for
Storage account. Then in the resulting Storage account page, select Create.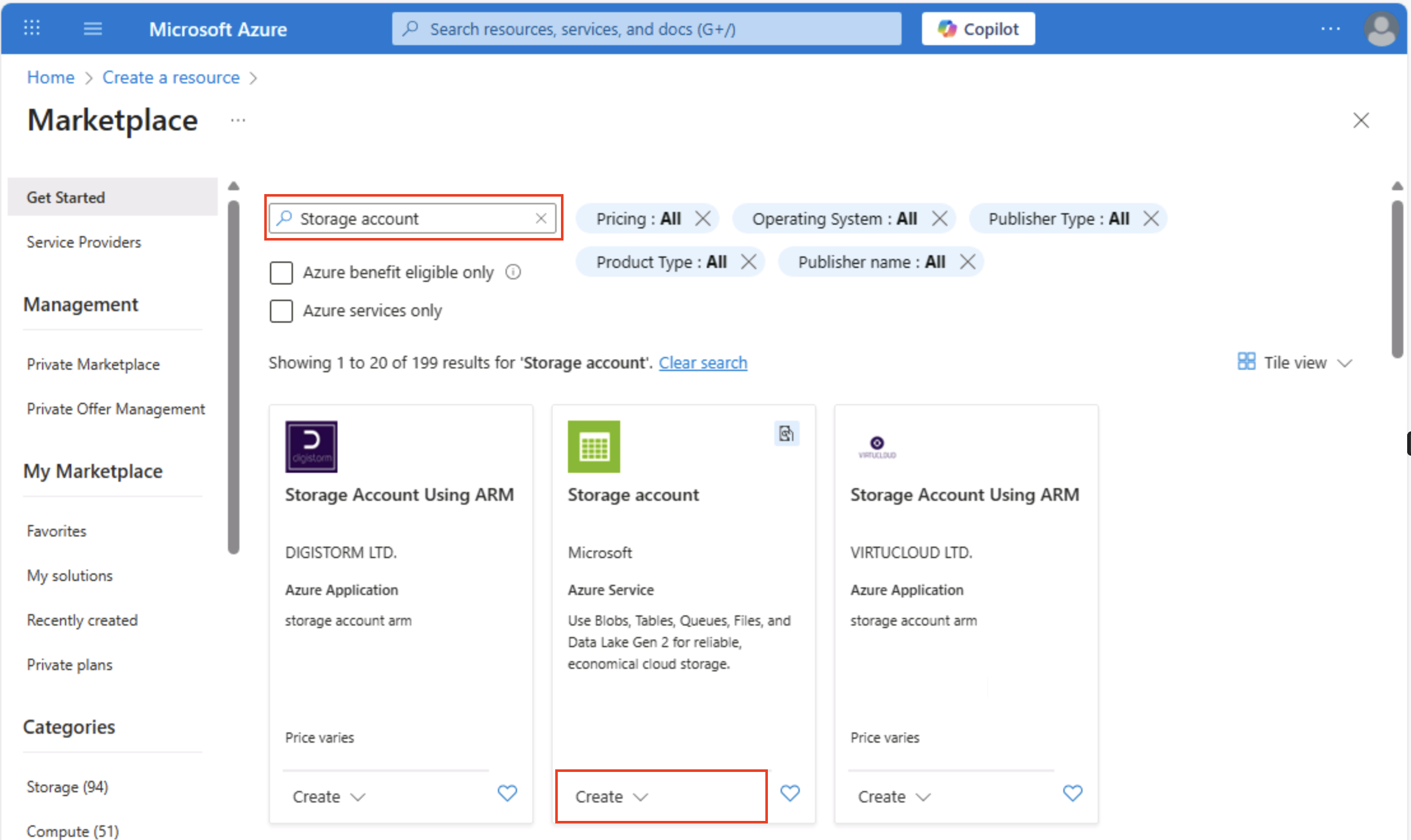
-
Enter the following values on the Create a storage account page:
- Subscription: Select your Azure subscription.
- Resource group: Create a new resource group with a name of your choice.
- Storage account name: Enter a unique name for your storage account using lower-case letters and numbers.
- Region: Select any available location.
- Performance: Standard
- Redundancy: Locally-redundant storage (LRS)
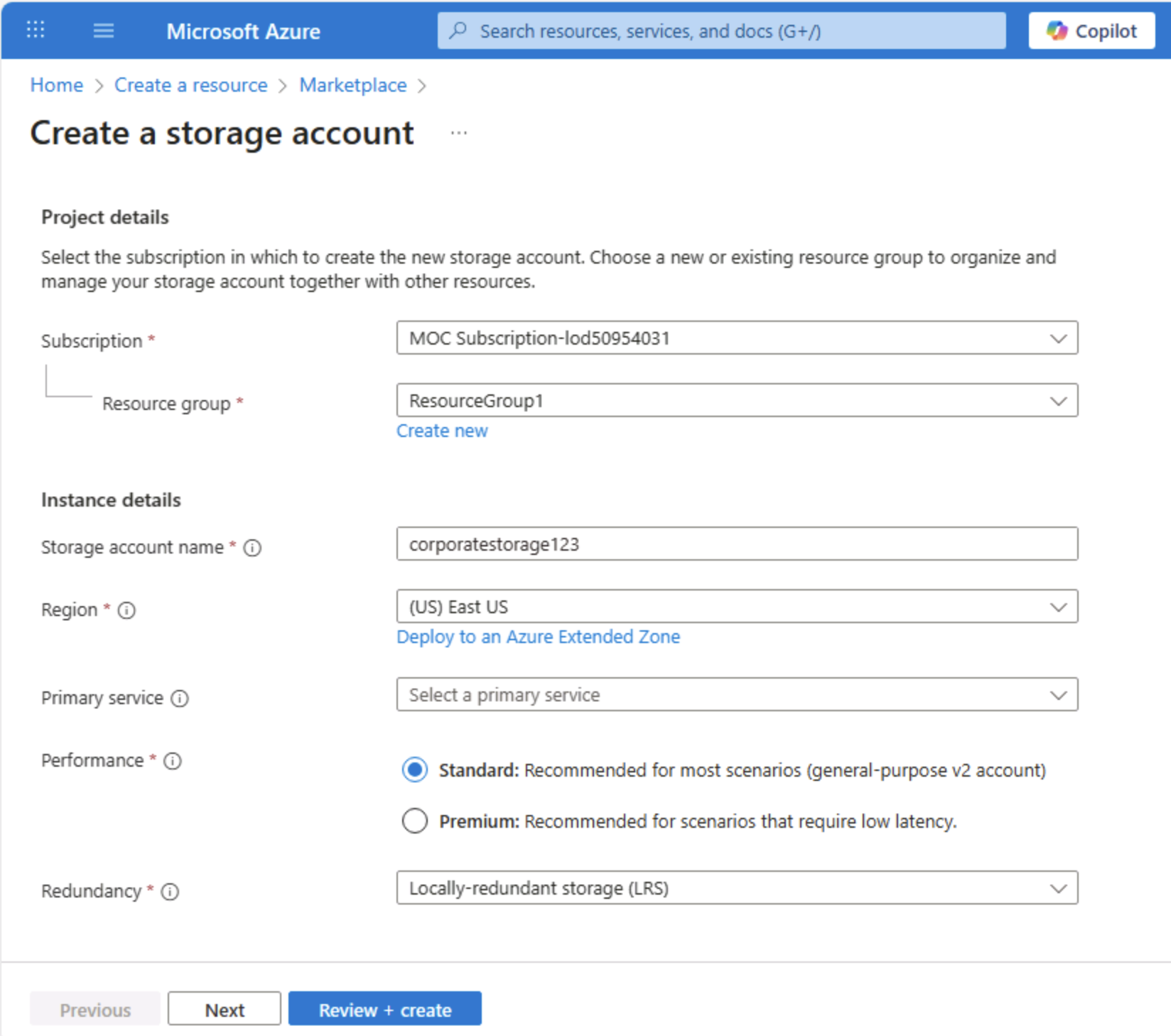
Tip: A new resource group makes cleanup easy. Standard + LRS is the lowest-cost baseline, good for learning. LRS keeps three synchronous copies in one region, adequate for non-critical demo data without paying for geo-replication.
-
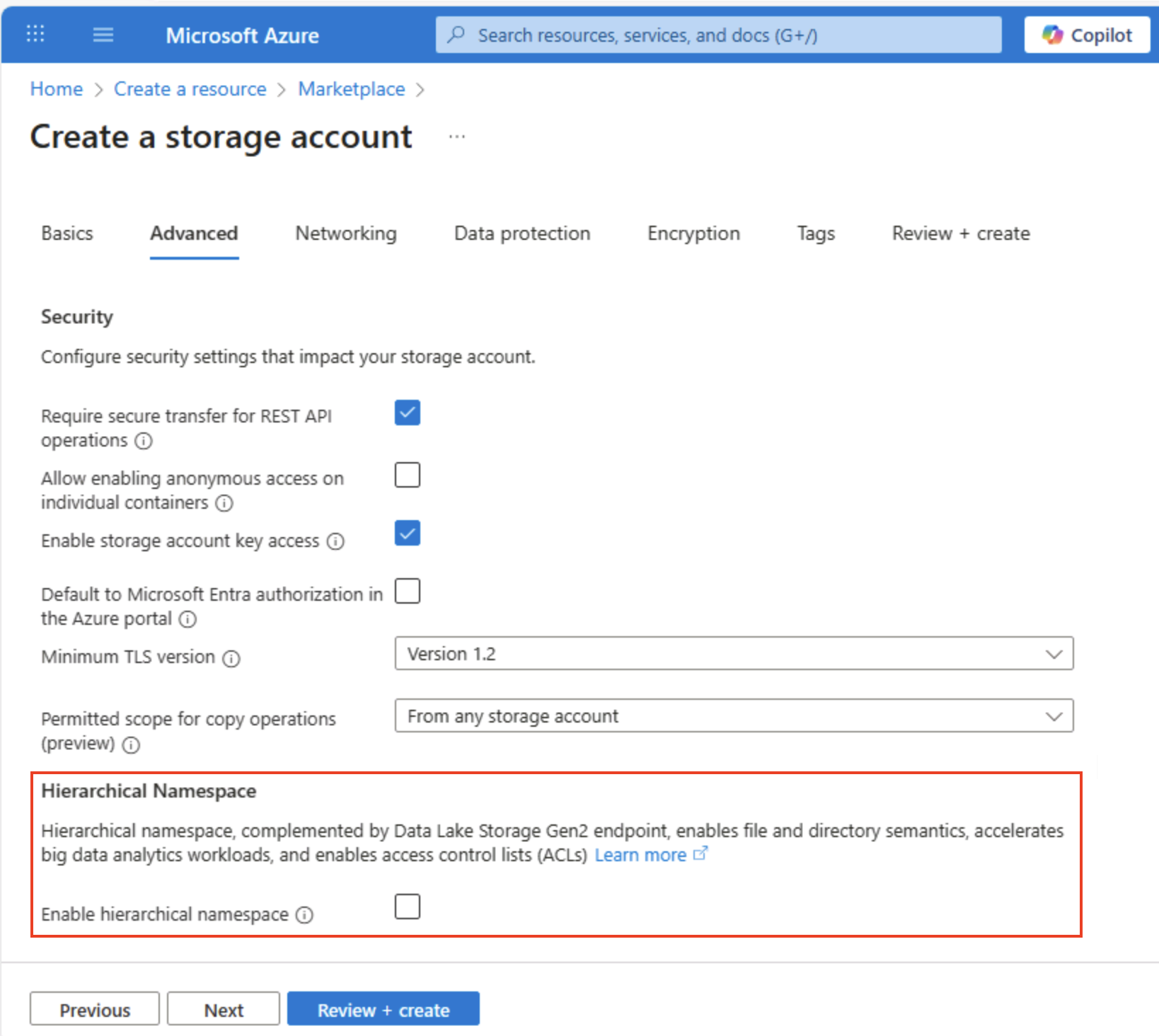
Select Next: Advanced > and view the advanced configuration options. In particular, note that this is where you can enable hierarchical namespace to support Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. Leave this option cleared (you’ll enable it later), and then select Next: Networking > to view the networking options for your storage account.
-
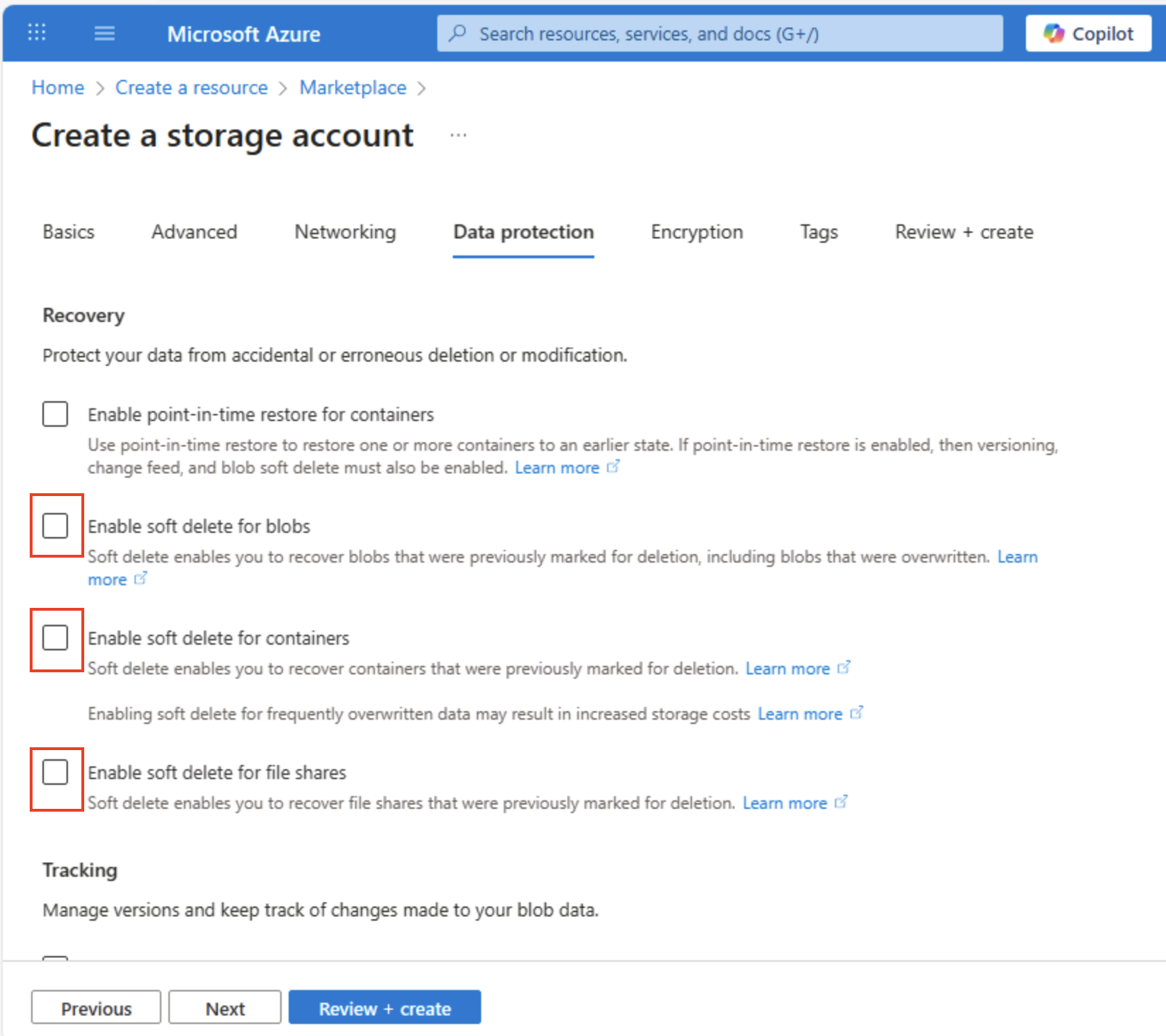
Select Next: Data protection > and then in the Recovery section, deselect all of the Enable soft delete… options. These options retain deleted files for subsequent recovery, but can cause issues later when you enable hierarchical namespace.
-
Continue through the remaining Next > pages without changing any of the default settings, and then on the Review page, wait for your selections to be validated and select Create to create your Azure Storage account.
-
Wait for deployment to complete. Then go to the resource that was deployed.
Explore blob storage
Now that you have an Azure Storage account, you can create a container for blob data.
Tip: A container groups blobs and is the first scoping level for access control. Starting with plain blob storage (no hierarchical namespace) shows virtual folder behavior you’ll compare to Data Lake Gen2 later.
-
Download the product1.json JSON file from
https://aka.ms/product1.jsonand save it on your computer (you can save it in any folder - you’ll upload it to blob storage later).If the JSON file is displayed in your browser, right click the page, and select Save As. Name the file product1.json and store it in your downloads folder.
-
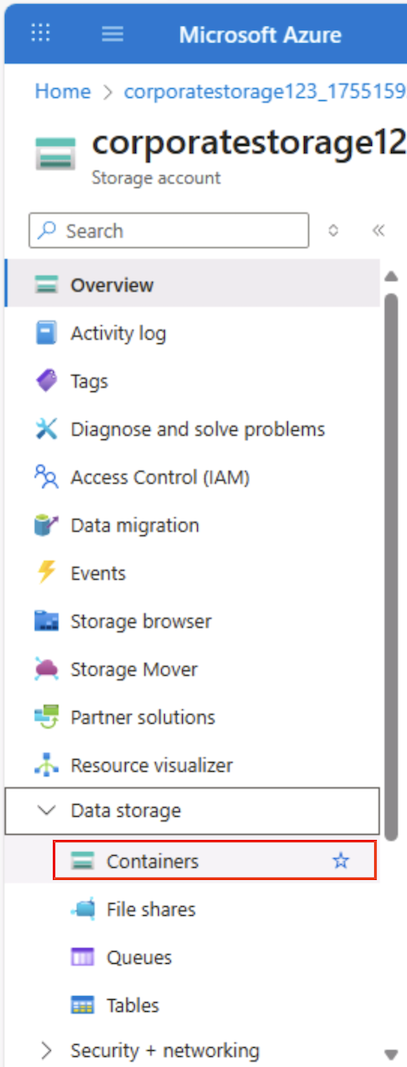
In the Azure portal page for your storage container, on the left side, in the Data storage section, select Containers.
-
In the Containers page, select + Add container and add a new container named
datawith an anonymous access level of Private (no anonymous access).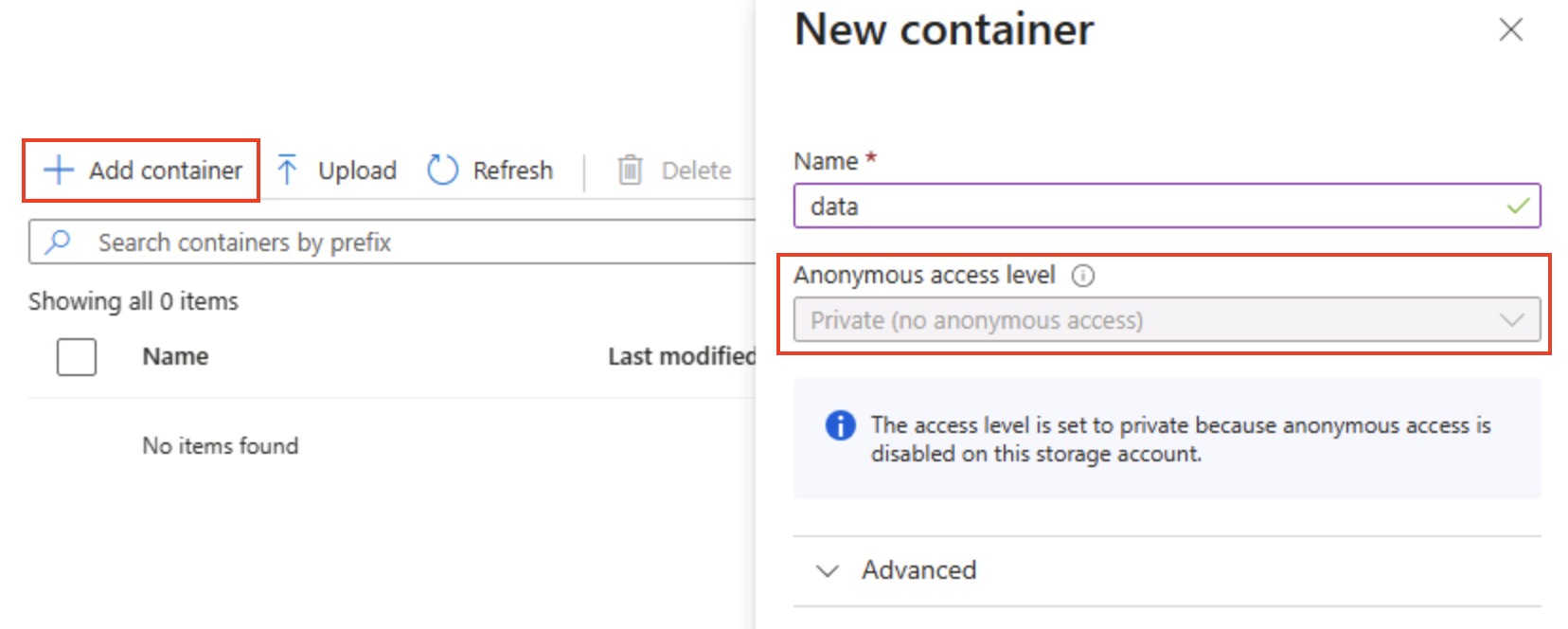
Tip: Private keeps your sample data secure. Public access is rarely needed except for static website or open data scenarios. Naming it
datakeeps this example simple and readable. -
When the data container has been created, verify that it’s listed in the Containers page.
-
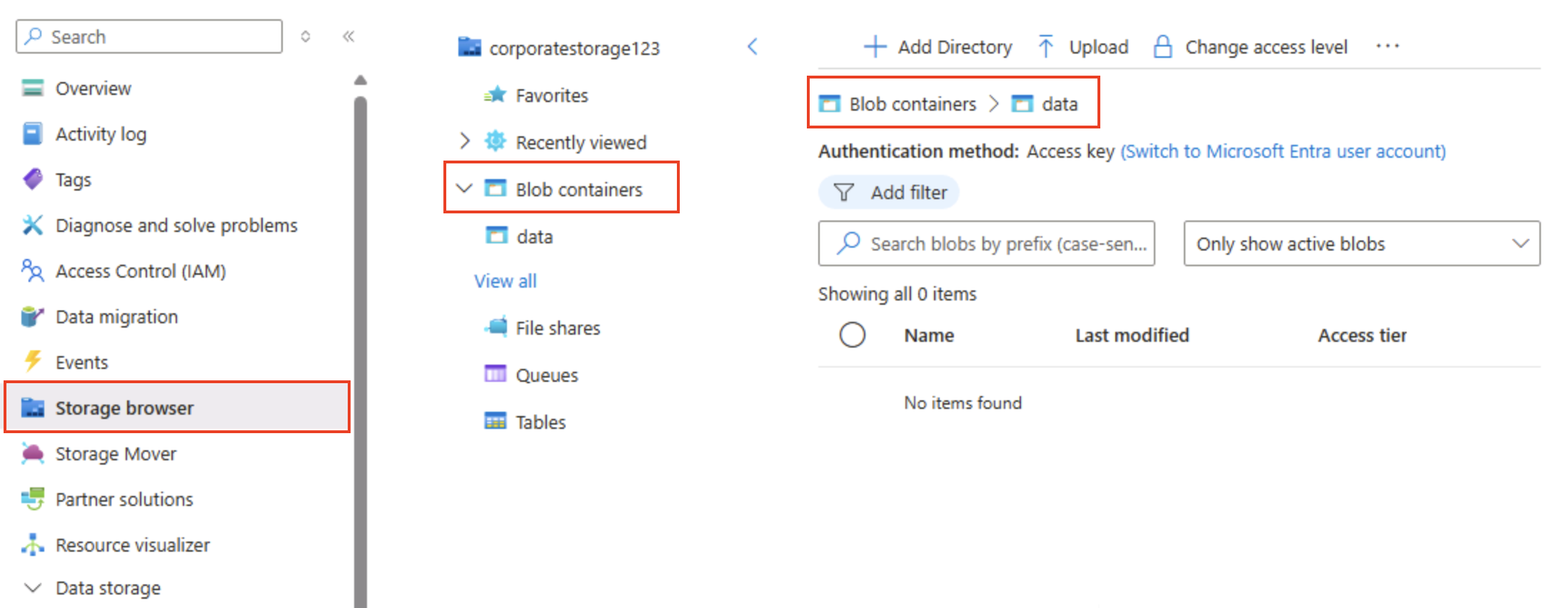
In the pane on the left side, in the top section, select Storage browser. This page provides a browser-based interface that you can use to work with the data in your storage account.
-
In the storage browser page, select Blob containers and verify that your data container is listed.
-
Select the data container, and note that it’s empty.
-
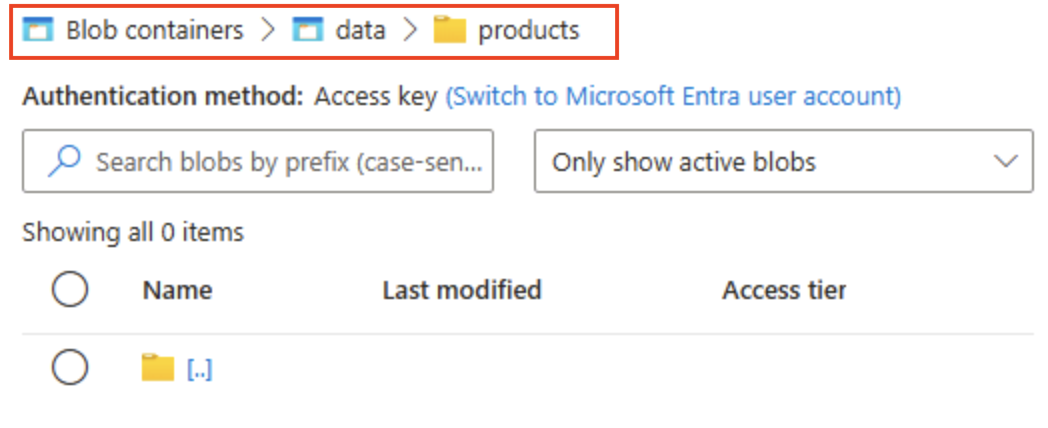
Select + Add Directory and read the information about folders before creating a new directory named
products. -
In storage browser, verify that the current view shows the contents of the products folder you just created - observe that the “breadcrumbs” at the top of the page reflect the path Blob containers > data > products.
-
In the breadcrumbs, select data to switch to the data container, and note that it does not contain a folder named products.
Folders in blob storage are virtual, and only exist as part of the path of a blob. Since the products folder contained no blobs, it isn’t really there!
Tip: Flat namespace means directories are just name prefixes (products/file.json). This design enables massive scale because the service indexes blob names instead of maintaining a true tree structure.
-
Use the ⤒ Upload button to open the Upload blob panel.
-
In the Upload blob panel, select the product1.json file you saved on your local computer previously. Then in the Advanced section, in the Upload to folder box, enter
product_dataand select the Upload button.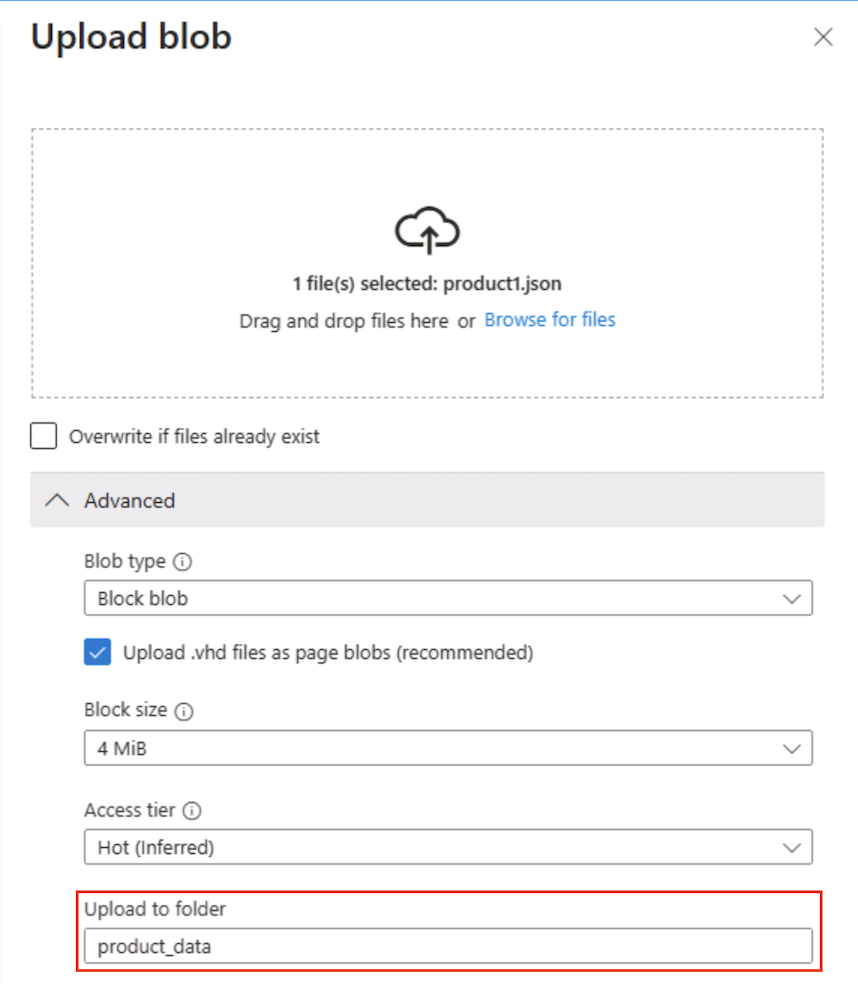
Tip: Supplying a folder name while uploading auto-creates the virtual path, illustrating that presence of a blob makes the “folder” appear.
-
Close the Upload blob panel if it’s still open, and verify that a product_data virtual folder has been created in the data container.
-
Select the product_data folder and verify that it contains the product1.json blob you uploaded.
-
On the left side, in the Data storage section, select Containers.
-
Open the data container, and verify that the product_data folder you created is listed.
-
Select the ‧‧‧ icon at the right-end of the folder, and note that the menu doesn’t display any options. Folders in a flat namespace blob container are virtual, and can’t be managed.
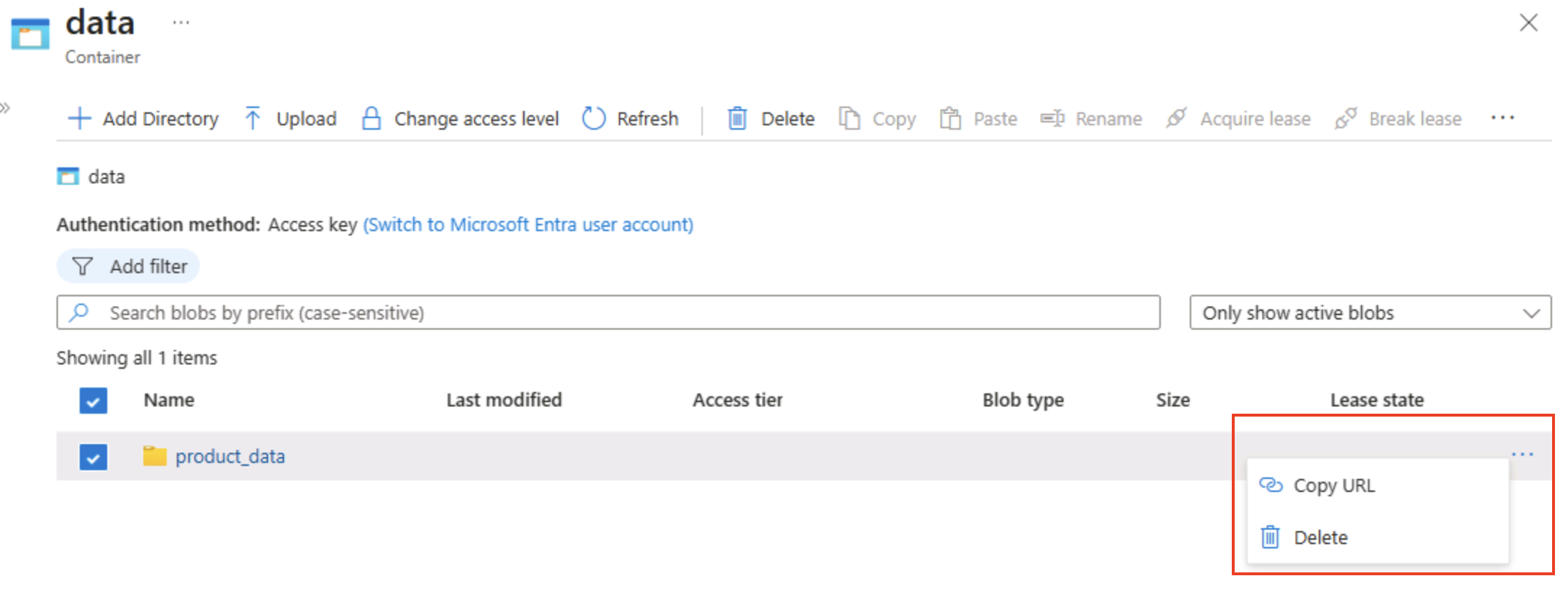
Tip: No real directory object exists, so there are no rename/permission operations — those require hierarchical namespace.
-
Use the X icon at the top right in the data page to close the page and return to the Containers page.
Explore Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
Azure Data Lake Store Gen2 support enables you to use hierarchical folders to organize and manage access to blobs. It also enables you to use Azure blob storage to host distributed file systems for common big data analytics platforms.
Tip: Turning on hierarchical namespace makes folders behave like real directories. It also lets you do folder actions safely (all at once, without errors) and gives you file-permission controls similar to those in Linux. This is especially helpful when working with big data tools like Spark or Hadoop, or when managing large, organized data lakes.
-
Download the product2.json JSON file from
https://aka.ms/product2.jsonand save it on your computer in the same folder where you downloaded product1.json previously - you’ll upload it to blob storage later. -
In the Azure portal page for your storage account, on the left side, scroll down to the Settings section, and select Data Lake Gen2 upgrade.
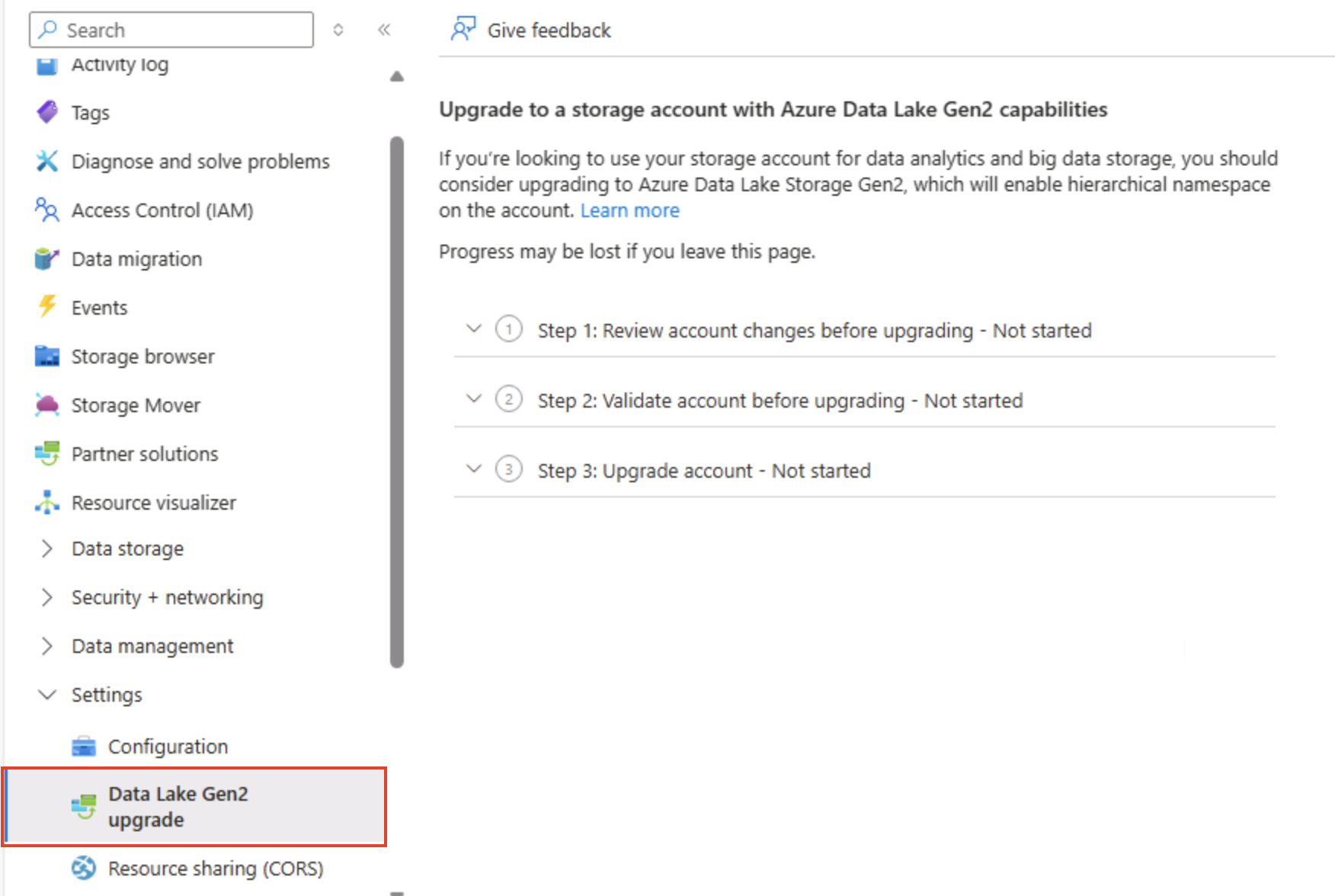
-
In the Data Lake Gen2 upgrade page, expand and complete each step to upgrade your storage account to enable hierarchical namespace and support Azure Data Lake Storage Gen. This may take some time.
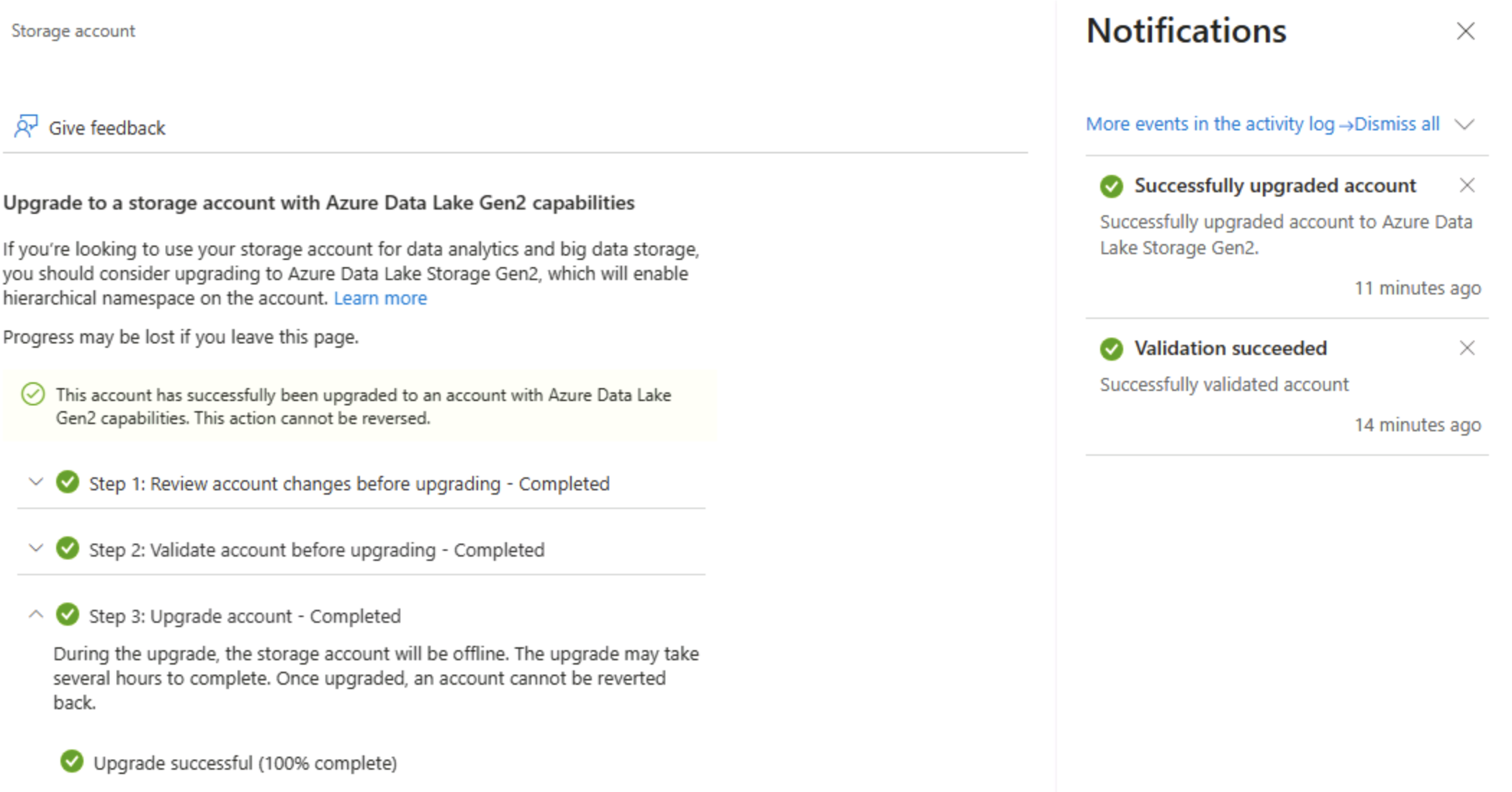
Tip: The upgrade is an account-level capability switch — data remains, but directory semantics change to support advanced operations.
-
When the upgrade is complete, in the pane on the left side, in the top section, select Storage browser and navigate back to the root of your data blob container, which still contains the product_data folder.
-
Select the product_data folder, and verify it still contains the product1.json file you uploaded previously.
-
Use the ⤒ Upload button to open the Upload blob panel.
-
In the Upload blob panel, select the product2.json file you saved on your local computer. Then select the Upload button.
-
Close the Upload blob panel if it’s still open, and verify that a product_data folder now contains the product2.json file.
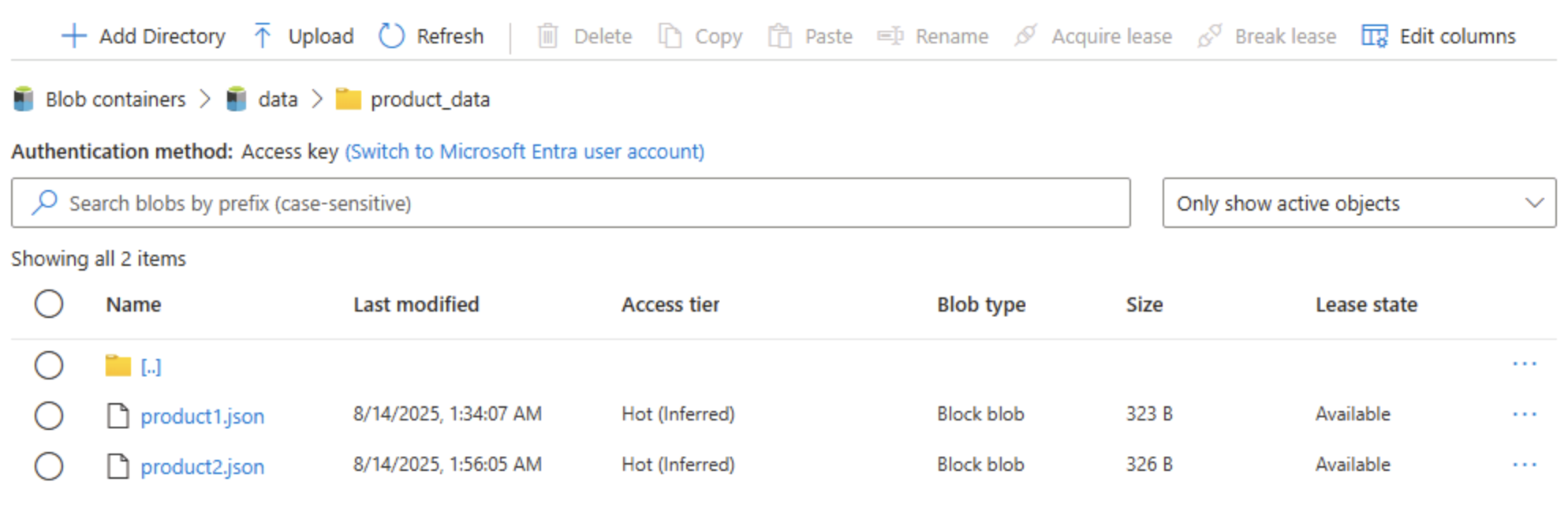
Tip: Adding a second file post-upgrade confirms seamless continuity: existing blobs still work, and new ones gain hierarchical benefits such as directory ACLs (Access Control Lists).
-
On the left side, in the Data storage section, select Containers.
-
Open the data container, and verify that the product_data folder you created is listed.
-
Select the ‧‧‧ icon at the right-end of the folder, and note that with hierarchical namespace enabled, you can perform configuration tasks at the folder-level; including renaming folders and setting permissions.
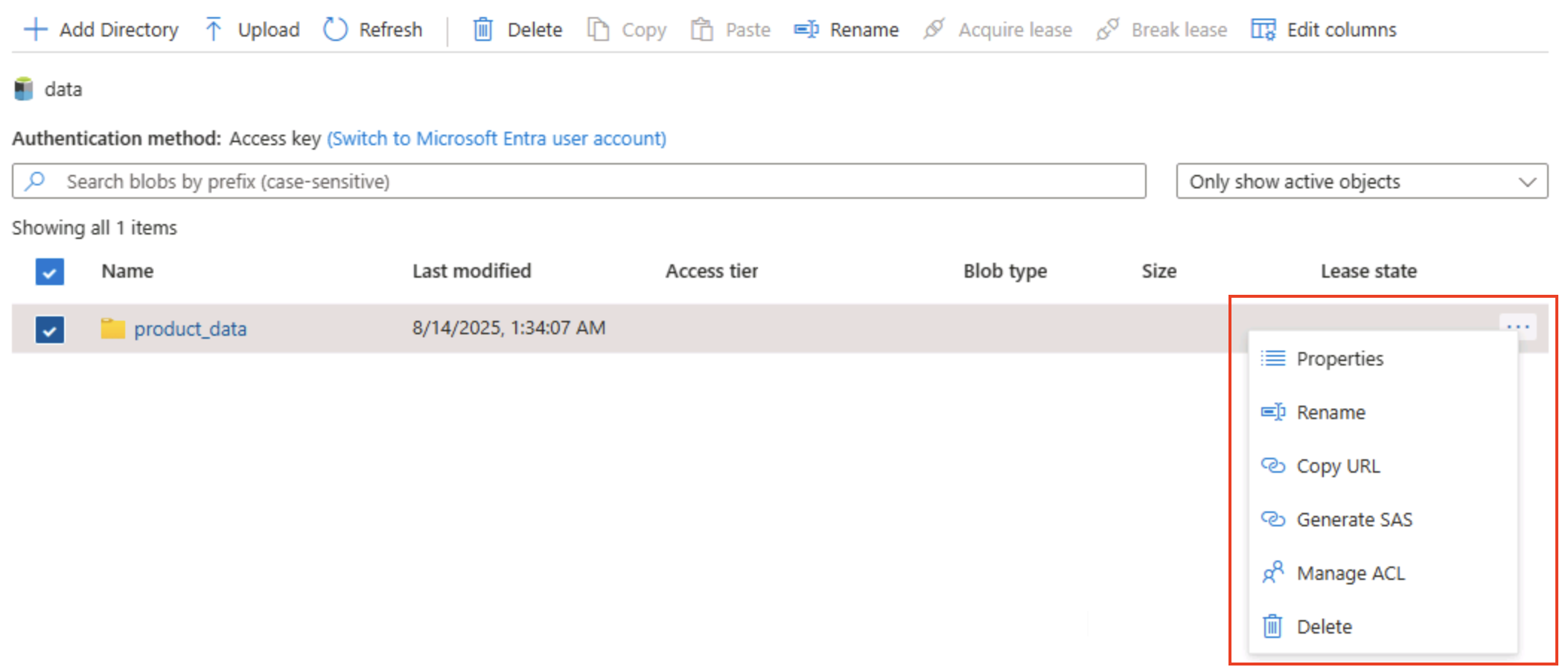
Tip: Real folders let you apply least-privilege security at folder granularity, rename safely, and speed recursive listings versus scanning thousands of prefixed blob names.
-
Use the X icon at the top right in the data page to close the page and return to the Containers page.
Explore Azure Files
Azure Files provides a way to create cloud-based file shares.
Tip: Azure Files offers SMB/NFS endpoints for lift‑and‑shift scenarios where apps expect a traditional file system. It complements (not replaces) blob storage by supporting file locks and OS-native tooling.
-
In the Azure portal page for your storage container, on the left side, in the Data storage section, select File shares.

-
In the File shares page, select + File share and add a new file share named
filesusing the Transaction optimized tier. -
Select Next: Backup > and disable backup. Then select Review + create.
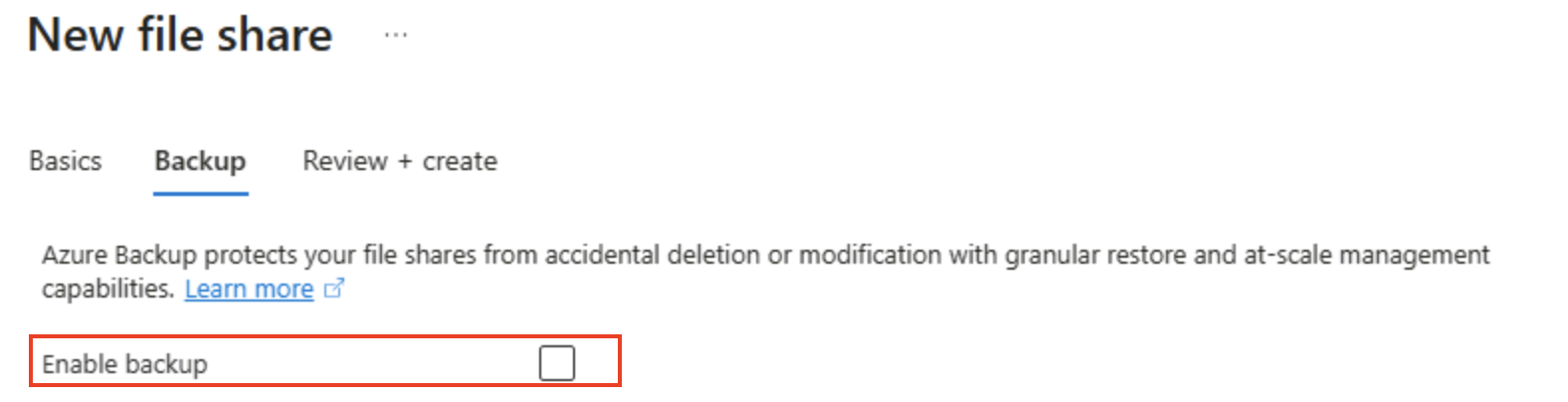
Tip: Disabling backup keeps costs down for a short-lived lab environment — you would enable it for production resilience.
-
In the File shares, open your new files share.
-
At the top of the page, select Connect. Then in the Connect pane, note that there are tabs for common operating systems (Windows, Linux, and macOS) that contain scripts you can run to connect to the shared folder from a client computer.
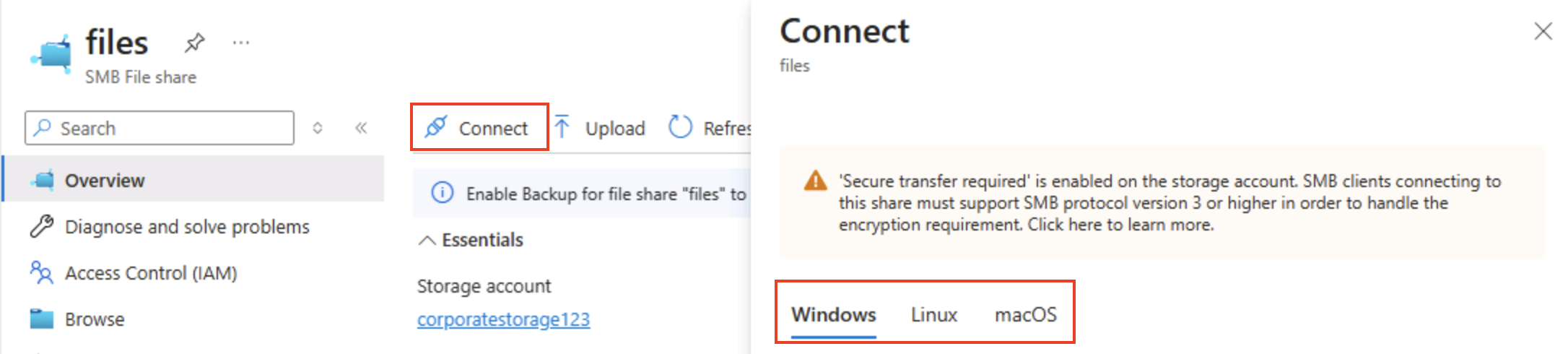
Tip: The generated scripts show exactly how to mount the share using platform-native commands, illustrating hybrid access patterns from virtual machines, containers, or on-prem servers.
-
Close the Connect pane and then close the files page to return to the File shares page for your Azure storage account.
Explore Azure Tables
Azure Tables provide a key/value store for applications that need to store data values, but don’t need the full functionality and structure of a relational database.
Tip: Table storage trades rich querying & joins for ultra-low cost, schemaless flexibility, and horizontal scale — ideal for logs, IoT data, or user profiles.
-
In the Azure portal page for your storage container, on the left side, in the Data storage section, select Tables.
-
On the Tables page, select + Table and create a new table named
products. -
After the products table has been created, in the pane on the left side, in the top section, select Storage browser.
-
In storage explorer, select Tables and verify that the products table is listed.
-
Select the products table.
-
In the product page, select + Add entity.
- In the Add entity panel, enter the following key values:
- PartitionKey: 1
- RowKey: 1
Tip: PartitionKey groups related entities to distribute load; RowKey uniquely identifies within the partition. Together they form a fast composite primary key for lookups.
-
Select Add property, and create two new properties with the following values:
Property name Type Value Name String Widget Price Double 2.99 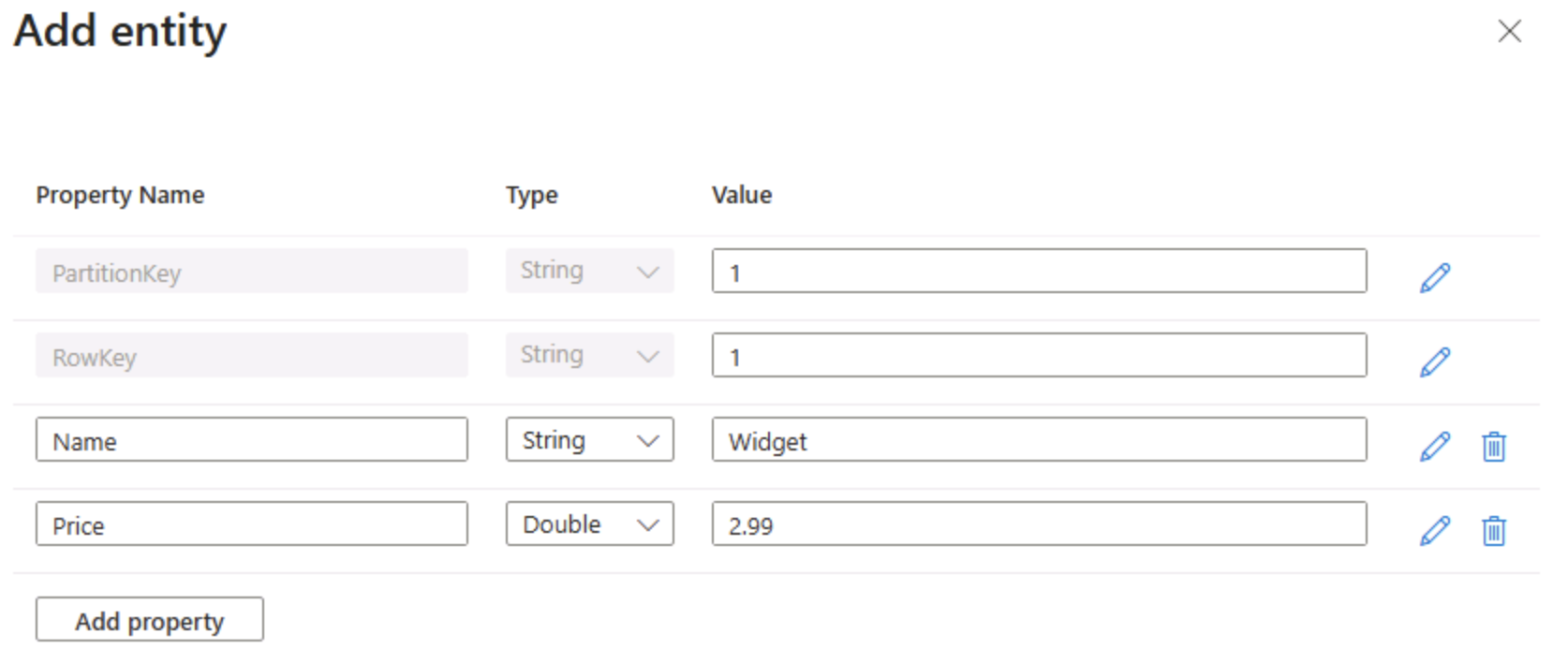
-
Select Insert to insert a row for the new entity into the table.
-
In storage browser, verify that a row has been added to the products table, and that a Timestamp column has been created to indicate when the row was last modified.
-
Add another entity to the products table with the following properties:
Property name Type Value PartitionKey String 1 RowKey String 2 Name String Kniknak Price Double 1.99 Discontinued Boolean true Tip: Adding a second entity with different keys and an extra Boolean property demonstrates schema-on-write flexibility — new attributes don’t require a migration.
-
After inserting the new entity, verify that a row containing the discontinued product is shown in the table.
You have manually entered data into the table using the storage browser interface. In a real scenario, application developers can use the Azure Storage Table API to build applications that read and write values to tables, making it a cost effective and scalable solution for NoSQL storage.
Tip: If you’ve finished exploring Azure Storage, you can delete the resource group that you created in this exercise. Deleting the resource group is the quickest way to avoid ongoing charges by removing every resource you created in one action.