Exercise 04: Configure network routing
Scenario
To ensure the firewall policies are enforced, outbound application traffic must be routed through the firewall. You identify these requirements.
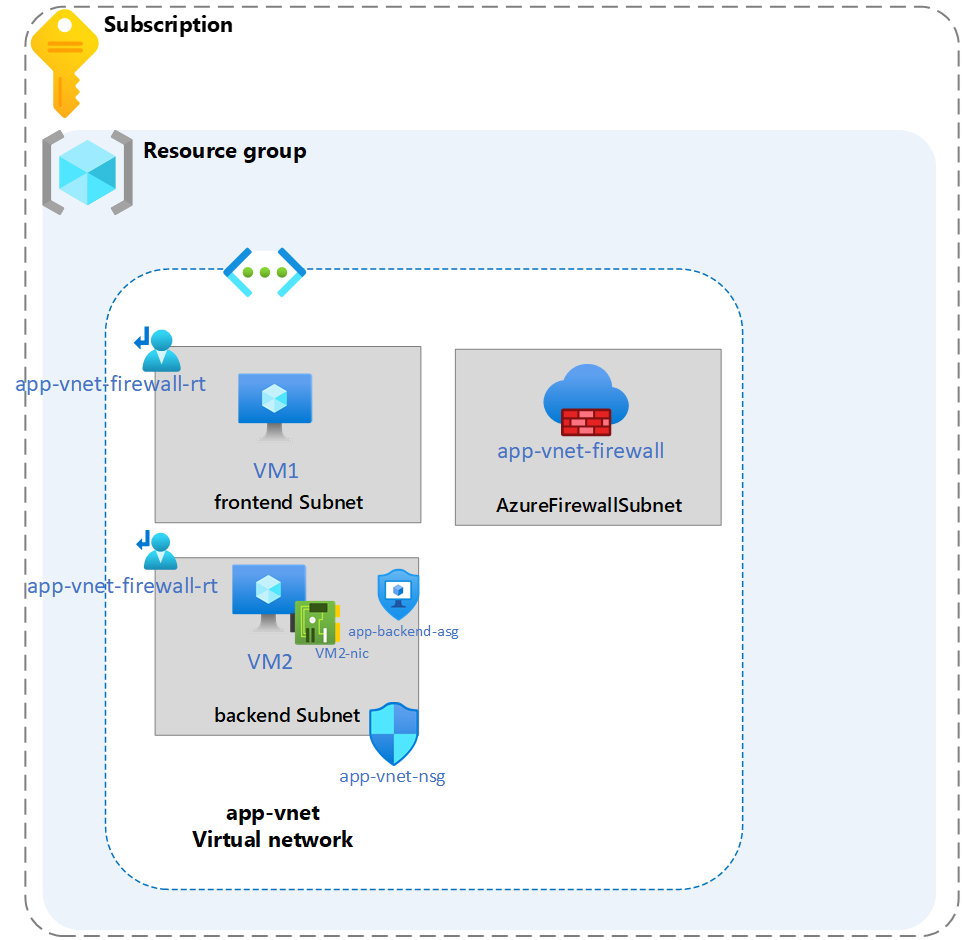
- A route table is required. This route table will be associated with the frontend and backend subnets.
- A route is required to filter all outbound IP traffic from the subnets to the firewall. The firewall’s private IP address will be used.
Skilling tasks
- Create and configure a route table.
- Link a route table to a subnet.
Architecture diagram
Estimated timing: 20 minutes
Exercise instructions
Create a route table
Azure automatically creates a route table for each subnet within an Azure virtual network. The route table includes the default system routes. You can create route tables and routes to override Azure’s default system routes.
Record the private IP address of app-vnet-firewall
-
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Firewall. Select Firewall in the search results.
-
Select app-vnet-firewall.
-
Select Overview and record the Private IP address.
Add the route table
-
In the search box, enter Route tables. When Route table appears in the search results, select it.
-
In the Route table page, select + Create and create the route table.
Property Value Subscription Select your subscription Resource group RG1 Region East US Name app-vnet-firewall-rt -
Select Review + create and then select Create.
-
Wait for the route table to deploy, then select Go to resource.
Associate the route table to the subnets
-
In the portal, continue working with the route table, select app-vnet-firewall-rt.
-
In the Settings blade, select Subnets and then + Associate.
-
Configure an association to the frontend subnet, then select OK.
Property Value Virtual network app-vnet (RG1) Subnet frontend -
Configure an association to the backend subnet, then select OK.
Property Value Virtual network app-vnet (RG1) Subnet backend
Create a route in the route table
-
In the portal, continue working with the route table, select app-vnet-firewall-rt.
-
In the Settings blade, select Routes and then + Add.
-
Configure the route, then select Add.
Property Value Route name outbound-firewall Destination type IP addresses Destination IP addresses/CIDR range 0.0.0.0/0 Next hop type Virtual appliance Next hop address private IP address of the firewall
Learn more with online training
- Manage and control traffic flow in your Azure deployment with routes. In this module, you learn how to control Azure virtual network traffic by implementing custom routes. This module has two sandboxes.
Key takeaways
Congratulations on completing the exercise. Here are the main takeaways:
- Network traffic in Azure is automatically routed across Azure subnets, virtual networks, and on-premises networks. System routes control this routing.
- User-defined routes override the default system routes so traffic can be routed through a network virtual appliances (NVAs).
- Network virtual appliances (NVAs) control the flow of network traffic. Examples of NVAs are firewalls, load balancers, and routers.
- Route tables contain routing information and are associated with a subnet.