M02-Unit 3 Create and configure a virtual network gateway
Exercise scenario
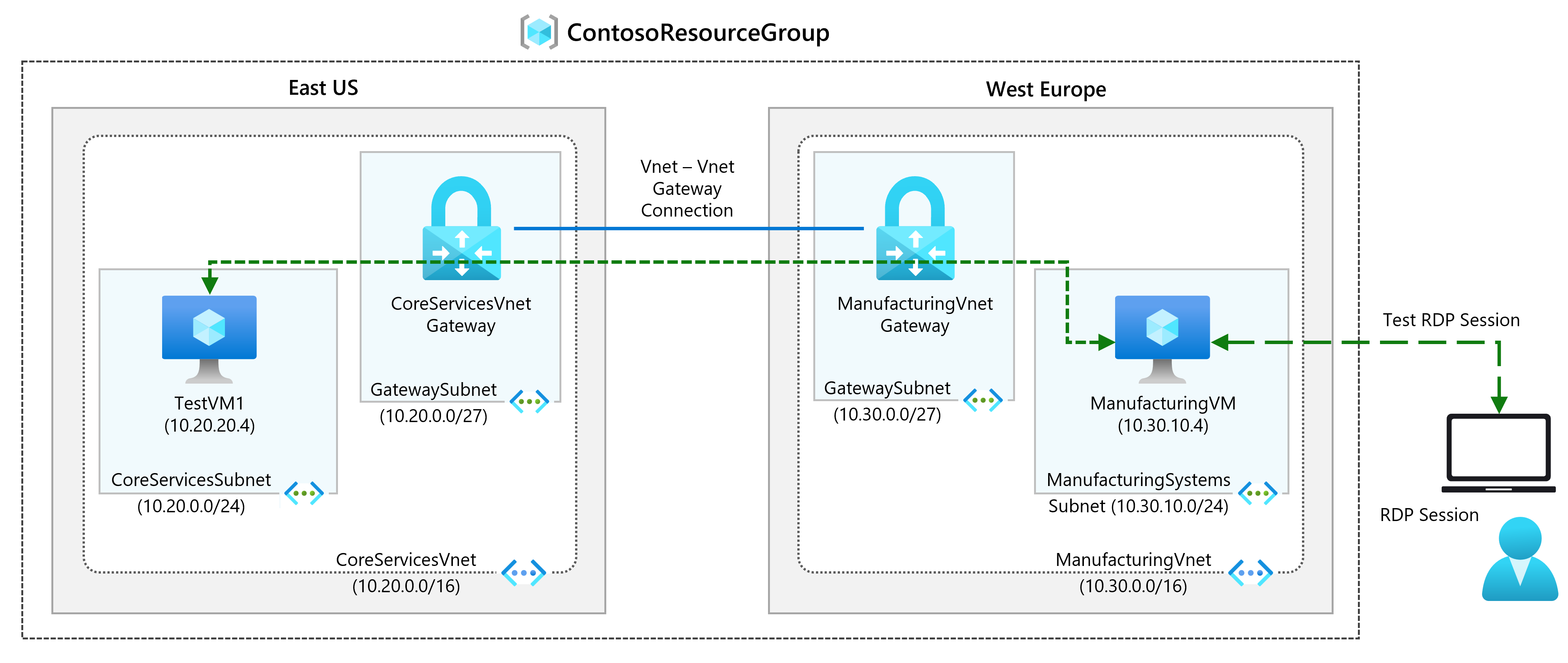
In this exercise you will configure a virtual network gateway to connect the Contoso Core Services VNet and Manufacturing VNet.
Job skills
In this exercise, you will:
- Task 1: Create CoreServicesVnet and ManufacturingVnet
- Task 2: Create CoreServicesVM
- Task 3: Create ManufacturingVM
- Task 4: Connect to the VMs using RDP
- Task 5: Test the connection between the VMs
- Task 6: Create CoreServicesVnet Gateway
- Task 7: Create ManufacturingVnet Gateway
- Task 8: Connect CoreServicesVnet to ManufacturingVnet
- Task 9: Connect ManufacturingVnet to CoreServicesVnet
- Task 10: Verify that the connections connect
- Task 11: Test the connection between the VMs
Estimated time: 70 minutes (including ~45 minutes deployment waiting time)
Task 1: Create CoreServicesVnet and ManufacturingVnet
- In the Azure portal, select the Cloud Shell icon (top right). If necessary, configure the shell.
- Select PowerShell.
- Select No Storage Account required and your Subscription, then select Apply.
- Wait for the terminal to create and a prompt to be displayed.
-
On the toolbar of the Cloud Shell pane, select the Manage files icon, in the drop-down menu, select Upload and upload the following files azuredeploy.json and azuredeploy.parameters.json into the Cloud Shell home directory.
Note:: If you are working in your own subscription the [template files](https://github.com/MicrosoftLearning/AZ-700-Designing-and-Implementing-Microsoft-Azure-Networking-Solutions/tree/master/Allfiles/Exercises) are available in the GitHub lab repository. -
Deploy the following ARM templates to create the virtual network and subnets needed for this exercise:
$RGName = "ContosoResourceGroup" #create resource group if it doesnt exist New-AzResourceGroup -Name $RGName -Location "eastus" New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $RGName -TemplateFile azuredeploy.json -TemplateParameterFile azuredeploy.parameters.json
Task 2: Create CoreServicesVM
-
On the Azure portal, open the PowerShell session within the Cloud Shell pane.
-
On the toolbar of the Cloud Shell pane, select the Manage files icon, in the drop-down menu, select Upload and upload the following files CoreServicesVMazuredeploy.json and CoreServicesVMazuredeploy.parameters.json into the Cloud Shell home directory one by one from the source folder F:\Allfiles\Exercises\M02.
-
Deploy the following ARM templates to create the VMs needed for this exercise:
Note: You will be prompted to provide an Admin password.
$RGName = "ContosoResourceGroup" New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $RGName -TemplateFile CoreServicesVMazuredeploy.json -TemplateParameterFile CoreServicesVMazuredeploy.parameters.json -
When the deployment is complete, go to the Azure portal home page, and then select Virtual Machines.
-
Verify that the virtual machine has been created.
Task 3: Create ManufacturingVM
-
On the Azure portal, open the PowerShell session within the Cloud Shell pane.
-
On the toolbar of the Cloud Shell pane, select the Manage files icon, in the drop-down menu, select Upload and upload the following files ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.json and ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.parameters.json into the Cloud Shell home directory one by one from the source folder F:\Allfiles\Exercises\M02.
-
Deploy the following ARM templates to create the VMs needed for this exercise:
Note: You will be prompted to provide an Admin password.
$RGName = "ContosoResourceGroup" New-AzResourceGroupDeployment -ResourceGroupName $RGName -TemplateFile ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.json -TemplateParameterFile ManufacturingVMazuredeploy.parameters.json -
When the deployment is complete, go to the Azure portal home page, and then select Virtual Machines.
-
Verify that the virtual machine has been created.
Task 4: Connect to the VMs using RDP
-
On the Azure Portal home page, select Virtual Machines.
-
Select ManufacturingVM.
-
On ManufacturingVM, select Connect and then RDP.
-
Select Download RDP file.
-
Save the RDP file to your desktop.
-
Connect to ManufacturingVM using the RDP file, and the username TestUser and the password you provided during deployment. After connecting, minimize the RDP session.
-
On the Azure Portal home page, select Virtual Machines.
-
Select CoreServicesVM.
-
On CoreServicesVM, select Connect and then RDP.
-
Select Download RDP file.
-
Save the RDP file to your desktop.
-
Connect to CoreServicesVM using the RDP file, and the username TestUser and the password you provided during deployment.
-
On both VMs, in Choose privacy settings for your device, select Accept.
-
On both VMs, in Networks, select Yes.
-
On CoreServicesVM, open PowerShell, and run the following command: ipconfig
-
Note the IPv4 address.
Task 5: Test the connection between the VMs
-
On the ManufacturingVM, open PowerShell.
-
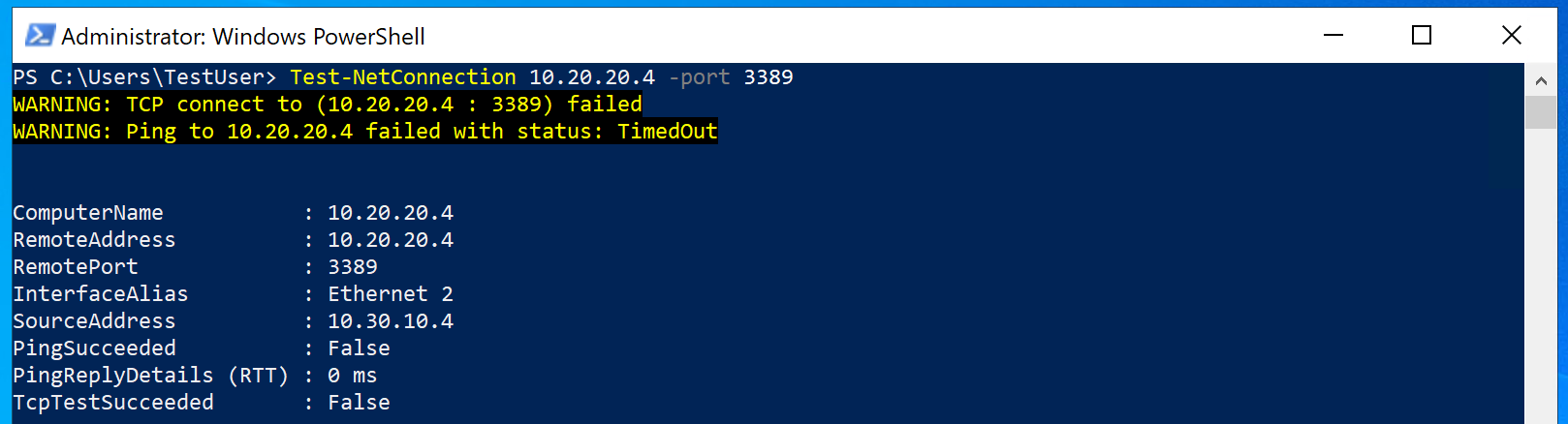
Use the following command to verify that there is no connection to CoreServicesVM on CoreServicesVnet. Be sure to use the IPv4 address for CoreServicesVM.
Test-NetConnection 10.20.20.4 -port 3389 -
The test connection should fail, and you will see a result similar to the following:
Task 6: Create CoreServicesVnet Gateway
-
In Search resources, services, and docs (G+/), enter Virtual network gateway, and then select Virtual network gateways from the results.
-
In Virtual network gateways, select + Create.
-
Use the information in the following table to create the virtual network gateway:
Tab Section Option Value Basics Project Details Subscription No changes required ResourceGroup ContosoResourceGroup Instance Details Name CoreServicesVnetGateway Region East US Gateway type VPN SKU VpnGw1AZ Generation Generation1 Virtual network CoreServicesVnet Subnet GatewaySubnet (10.20.0.0/27) Public IP address type Standard Public IP address Public IP address Create new Public IP address name CoreServicesVnetGateway-ip Enable active-active mode Disabled Configure BGP Disabled Review + create Review your settings and select Create. Note: It can take up to 15 - 30 minutes to create a virtual network gateway. You don’t need to wait for the deployment to complete. Proceed to creating the next gateway.
Task 7: Create ManufacturingVnet Gateway
Create the GatewaySubnet
Note: The template created the GatewaySubnet for the CoreServicesVnet. Here you create the subnet manually.
-
Search for and select the ManufacturingVnet.
-
In the Settings blade, select Subnets, and then + Subnet.
Parameter Value Subnet purpose Virtual Network Gateway Size /27 (32 addresses) -
Select Add.
Create the virtual network gateway
-
In Search resources, services, and docs (G+/), enter Virtual network gateway, and then select Virtual network gateways from the results.
-
In Virtual network gateways, select + Create.
-
Use this information and the Settings tab to create the virtual network gateway.
Tab Section Option Value Basics Project Details Subscription No changes required ResourceGroup ContosoResourceGroup Instance Details Name ManufacturingVnetGateway Region West Europe Gateway type VPN SKU VpnGw1AZ Generation Generation1 Virtual network ManufacturingVnet Subnet GatewaySubnet Public IP Address Type Standard Public IP address Public IP address Create new Public IP address name ManufacturingVnetGateway-ip Enable active-active mode Disabled Configure BGP Disabled Review + create Review your settings and select Create. Note: It can take up to 15 -30 minutes to create a virtual network gateway.
Task 8: Connect CoreServicesVnet to ManufacturingVnet
-
In Search resources, services, and docs (G+/), enter Virtual network gateway, and then select Virtual network gateways from the results.
-
In Virtual network gateways, select CoreServicesVnetGateway.
-
In CoreServicesGateway, select Connections, and then select + Add.
Note: You will not be able to complete this configuration until the virtual network gateways are fully deployed.
-
Use this information and the Settings tab to create the virtual network gateway.
Option Value Name CoreServicesGW-to-ManufacturingGW Connection type VNet-to-VNet Region East US First virtual network gateway CoreServicesVnetGateway Second virtual network gateway ManufacturingVnetGateway Shared key (PSK) abc123 Use Azure Private IP Address Not selected Enable BGP Not selected IKE Protocol IKEv2 Subscription No changes required Resource group No changes required -
To create the connection, select Review + Create and then Create.
Task 9: Connect ManufacturingVnet to CoreServicesVnet
-
In Search resources, services, and docs (G+/), enter Virtual network gateway, and then select Virtual network gateways from the results.
-
In Virtual network gateways, select ManufacturingVnetGateway.
-
In CoreServicesGateway, select Connections, and then select + Add.
-
Use the information in the following table to create the connection:
Option Value Name ManufacturingGW-to-CoreServicesGW Connection type VNet-to-VNet Location West Europe First virtual network gateway ManufacturingVnetGateway Second virtual network gateway CoreServicesVnetGateway Shared key (PSK) abc123 Use Azure Private IP Address Not selected Enable BGP Not selected IKE Protocol IKEv2 Subscription No changes required Resource group No changes required -
To create the connection, select Review + Create and then Create.
Task 10: Verify that the connections connect
-
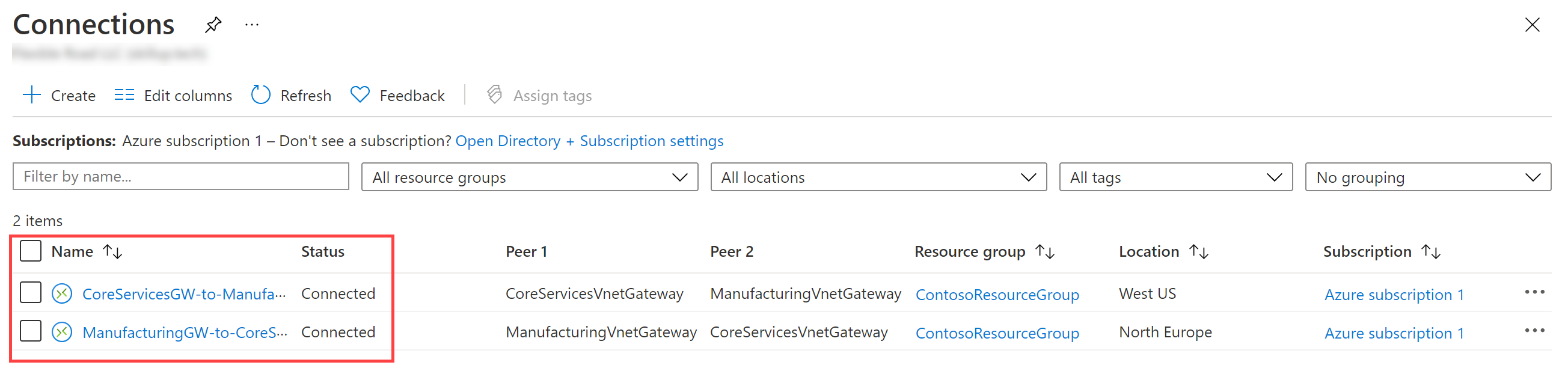
In Search resources, services, and docs (G+/), enter vpn, and then select connections from the results.
-
Wait until the status of both connections is Connected. You may need to refresh your screen.
Task 11: Test the connection between the VMs
-
On the ManufacturingVM, open PowerShell.
-
Use the following command to verify that there is now a connection to CoreServicesVM on CoreServicesVnet. Be sure to use the IPv4 address for CoreServicesVM.
Test-NetConnection 10.20.20.4 -port 3389 -
The test connection should succeed, and you will see a result similar to the following:
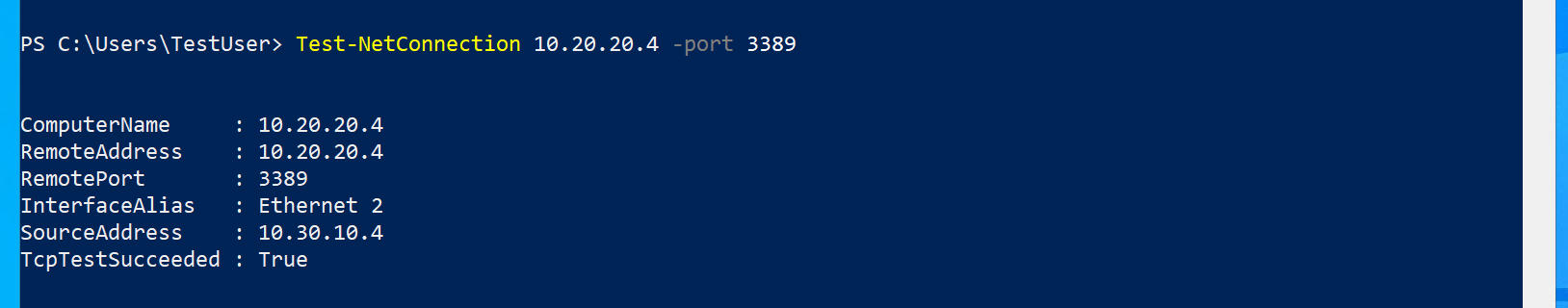
-
Close the Remote Desktop connection windows.
Extend your learning with Copilot
Copilot can assist you in learning how to use the Azure scripting tools. Copilot can also assist in areas not covered in the lab or where you need more information. Open an Edge browser and choose Copilot (top right) or navigate to copilot.microsoft.com. Take a few minutes to try these prompts.
- What are the main types of Azure VPN gateways and why would you use each type?
- What factors should I consider when selecting the Azure VPN gateway sku? Give examples.
- Are there costs associated with Azure VPN gateways?
Learn more with self-paced training
- Connect your on-premises network to Azure with VPN Gateway. In this module, you will how to use CLI to provision VPN gateways.
- Troubleshoot VPN gateways in Microsoft Azure. In this module, you learn how to monitor and troubleshoot site-to-site and point-to-site VPNs.
Key takeaways
Congratulations on completing the lab. Here are the main takeaways for this lab.
- Azure VPN Gateway is a service that provides secure connectivity between your on-premises networks and Azure virtual networks.
- Site-to-Site (S2S) connections connect your on-premises network to an Azure virtual network using IPsec/IKE VPN tunnels. Ideal for hybrid cloud scenarios.
- Point-to-Site (P2S) connections connnect individual clients to an Azure virtual network from remote locations. VPN protocols inlcude OpenVPN, IKEv2, or SSTP. Useful for remote workers.
- VNet-to-VNet connections connect two or more Azure virtual networks using IPsec/IKE VPN tunnels. Suitable for multi-region or multi-VNet deployments.
- Different VPN Gateway SKUs offer varying levels of performance, throughput, and features.