Classify Images with Azure AI Custom Vision
The Azure AI Custom Vision service enables you to create computer vision models that are trained on your own images. You can use it to train image classification and object detection models; which you can then publish and consume from applications.
In this exercise, you will use the Custom Vision service to train an image classification model that can identify three classes of fruit (apple, banana, and orange).
Clone the repository for this course
If you have not already cloned AI-102-AIEngineer code repository to the environment where you’re working on this lab, follow these steps to do so. Otherwise, open the cloned folder in Visual Studio Code.
- Start Visual Studio Code.
- Open the palette (SHIFT+CTRL+P) and run a Git: Clone command to clone the
https://github.com/MicrosoftLearning/AI-102-AIEngineerrepository to a local folder (it doesn’t matter which folder). - When the repository has been cloned, open the folder in Visual Studio Code.
-
Wait while additional files are installed to support the C# code projects in the repo.
Note: If you are prompted to add required assets to build and debug, select Not Now.
Create Custom Vision resources
Before you can train a model, you will need Azure resources for training and prediction. You can create Custom Vision resources for each of these tasks, or you can create a single Azure AI Services resource and use it for either (or both).
In this exercise, you’ll create Custom Vision resources for training and prediction so that you can manage access and costs for these workloads separately.
- In a new browser tab, open the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.com, and sign in using the Microsoft account associated with your Azure subscription. - Select the +Create a resource button, search for custom vision, and create a Custom Vision resource with the following settings:
- Create options: Both
- Subscription: Your Azure subscription
- Resource group: Choose or create a resource group (if you are using a restricted subscription, you may not have permission to create a new resource group - use the one provided)
- Region: Choose any available region
- Name: Enter a unique name
- Training pricing tier: F0
- Prediction pricing tier: F0
Note: If you already have an F0 custom vision service in your subscription, select S0 for this one.
- Wait for the resources to be created, and then view the deployment details and note that two Custom Vision resources are provisioned; one for training, and another for prediction (evident by the -Prediction suffix). You can view these by navigating to the resource group where you created them.
Important: Each resource has its own endpoint and keys, which are used to manage access from your code. To train an image classification model, your code must use the training resource (with its endpoint and key); and to use the trained model to predict image classes, your code must use the prediction resource (with its endpoint and key).
Create a Custom Vision project
To train an image classification model, you need to create a Custom Vision project based on your training resource. To do this, you’ll use the Custom Vision portal.
- In Visual Studio Code, view the training images in the 17-image-classification/training-images folder where you cloned the repository. This folder contains subfolders of apple, banana, and orange images.
- In a new browser tab, open the Custom Vision portal at
https://customvision.ai. If prompted, sign in using the Microsoft account associated with your Azure subscription and agree to the terms of service. - In the Custom Vision portal, create a new project with the following settings:
- Name: Classify Fruit
- Description: Image classification for fruit
- Resource: The Custom Vision resource you created previously
- Project Types: Classification
- Classification Types: Multiclass (single tag per image)
- Domains: Food
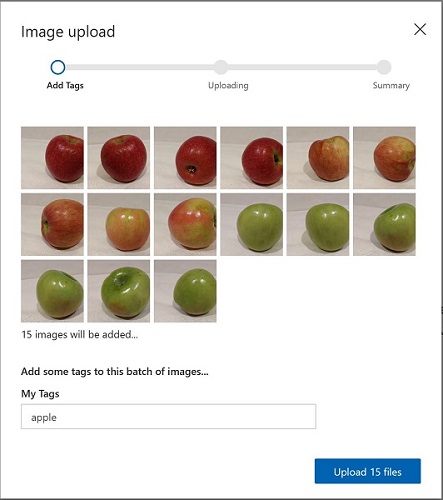
- In the new project, click [+] Add images, and select all of the files in the training-images/apple folder you viewed previously. Then upload the image files, specifying the tag apple, like this:
- Repeat the previous step to upload the images in the banana folder with the tag banana, and the images in the orange folder with the tag orange.
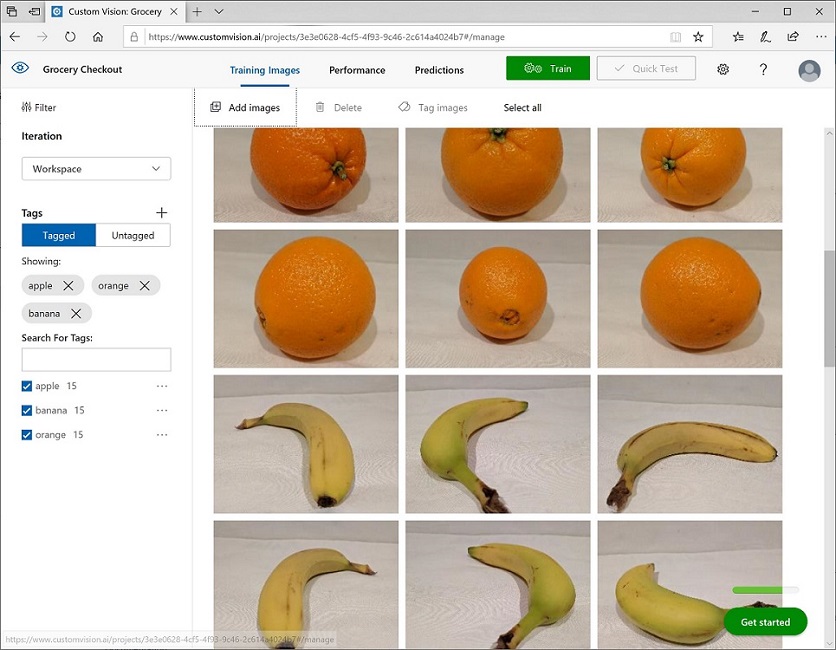
- Explore the images you have uploaded in the Custom Vision project - there should be 15 images of each class, like this:
- In the Custom Vision project, above the images, click Train to train a classification model using the tagged images. Select the Quick Training option, and then wait for the training iteration to complete (this may take a minute or so).
- When the model iteration has been trained, review the Precision, Recall, and AP performance metrics - these measure the prediction accuracy of the classification model, and should all be high.
Note: The performance metrics are based on a probability threshold of 50% for each prediction (in other words, if the model calculates a 50% or higher probability that an image is of a particular class, then that class is predicted). You can adjust this at the top-left of the page.
Test the model
Now that you’ve trained the model, you can test it.
- Above the performance metrics, click Quick Test.
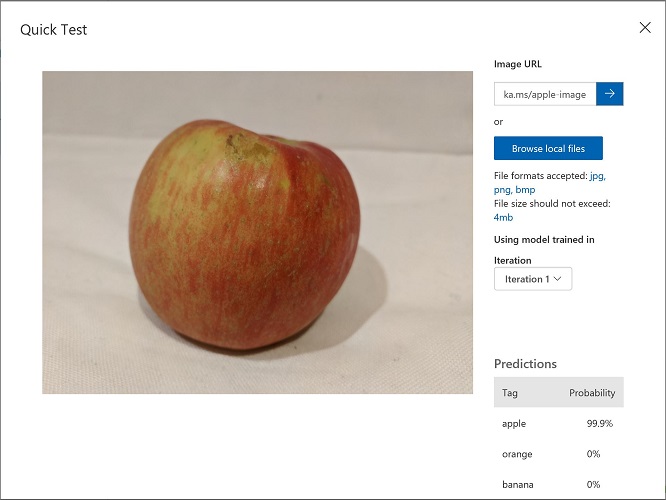
- In the Image URL box, type
https://aka.ms/apple-imageand click ➔ - View the predictions returned by your model - the probability score for apple should be the highest, like this:
- Close the Quick Test window.
View the project settings
The project you have created has been assigned a unique identifier, which you will need to specify in any code that interacts with it.
- Click the settings (⚙) icon at the top right of the Performance page to view the project settings.
- Under General (on the left), note the Project Id that uniquely identifies this project.
- On the right, under Resources note that the key and endpoint are shown. These are the details for the training resource (you can also obtain this information by viewing the resource in the Azure portal).
Use the training API
The Custom Vision portal provides a convenient user interface that you can use to upload and tag images, and train models. However, in some scenarios you may want to automate model training by using the Custom Vision training API.
Note: In this exercise, you can choose to use the API from either the C# or Python SDK. In the steps below, perform the actions appropriate for your preferred language.
- In Visual Studio Code, in the Explorer pane, browse to the 17-image_classification folder and expand the C-Sharp or Python folder depending on your language preference.
- Right-click the train-classifier folder and open an integrated terminal. Then install the Custom Vision Training package by running the appropriate command for your language preference:
C#
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Vision.CustomVision.Training --version 2.0.0
Python
pip install azure-cognitiveservices-vision-customvision==3.1.0
- View the contents of the train-classifier folder, and note that it contains a file for configuration settings:
- C#: appsettings.json
- Python: .env
Open the configuration file and update the configuration values it contains to reflect the endpoint and key for your Custom Vision training resource, and the project ID for the classification project you created previously. Save your changes.
-
Note that the train-classifier folder contains a code file for the client application:
- C#: Program.cs
- Python: train-classifier.py
Open the code file and review the code it contains, noting the following details:
- Namespaces from the package you installed are imported
- The Main function retrieves the configuration settings, and uses the key and endpoint to create an authenticated CustomVisionTrainingClient, which is then used with the project ID to create a Project reference to your project.
- The Upload_Images function retrieves the tags that are defined in the Custom Vision project and then uploads image files from correspondingly named folders to the project, assigning the appropriate tag ID.
- The Train_Model function creates a new training iteration for the project and waits for training to complete.
- Return the integrated terminal for the train-classifier folder, and enter the following command to run the program:
C#
dotnet run
Python
python train-classifier.py
- Wait for the program to end. Then return to your browser and view the Training Images page for your project in the Custom Vision portal (refreshing the browser if necessary).
- Verify that some new tagged images have been added to the project. Then view the Performance page and verify that a new iteration has been created.
Publish the image classification model
Now you’re ready to publish your trained model so that it can be used from a client application.
- In the Custom Vision portal, on the Performance page, click 🗸 Publish to publish the trained model with the following settings:
- Model name: fruit-classifier
- Prediction Resource: The prediction resource you created previously which ends with “-Prediction” (not the training resource).
- At the top left of the Project Settings page, click the Projects Gallery (👁) icon to return to the Custom Vision portal home page, where your project is now listed.
- On the Custom Vision portal home page, at the top right, click the settings (⚙) icon to view the settings for your Custom Vision service. Then, under Resources, find your prediction resource which ends with “-Prediction” (not the training resource) to determine its Key and Endpoint values (you can also obtain this information by viewing the resource in the Azure portal).
Use the image classifier from a client application
Now that you’ve published the image classification model, you can use it from a client application. Once again, you can choose to use C# or Python.
- In Visual Studio Code, in the 17-image-classification folder, in the subfolder for your preferred language (C-Sharp or Python), right- the test-classifier folder and open an integrated terminal. Then enter the following SDK-specific command to install the Custom Vision Prediction package:
C#
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.CognitiveServices.Vision.CustomVision.Prediction --version 2.0.0
Python
pip install azure-cognitiveservices-vision-customvision==3.1.0
Note: The Python SDK package includes both training and prediction packages, and may already be installed.
- Expand the test-classifier folder to view the files it contains, which are used to implement a test client application for your image classification model.
- Open the configuration file for your client application (appsettings.json for C# or .env for Python) and update the configuration values it contains to reflect the endpoint and key for your Custom Vision prediction resource, the project ID for the classification project, and the name of your published model (which should be fruit-classifier). Save your changes.
- Open the code file for your client application (Program.cs for C#, test-classification.py for Python) and review the code it contains, noting the following details:
- Namespaces from the package you installed are imported
- The Main function retrieves the configuration settings, and uses the key and endpoint to create an authenticated CustomVisionPredictionClient.
- The prediction client object is used to predict a class for each image in the test-images folder, specifying the project ID and model name for each request. Each prediction includes a probability for each possible class, and only predicted tags with a probability greater than 50% are displayed.
- Return the integrated terminal for the test-classifier folder, and enter the following SDK-specific command to run the program:
C#
dotnet run
Python
python test-classifier.py
- View the label (tag) and probability scores for each prediction. You can view the images in the test-images folder to verify that the model has classified them correctly.
More information
For more information about image classification with the Custom Vision service, see the Custom Vision documentation.